Computationally designed Spike antigens induce neutralising responses against the breadth of SARS-COV-2 variants
- PMID: 39251608
- PMCID: PMC11384739
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-024-00950-9
Computationally designed Spike antigens induce neutralising responses against the breadth of SARS-COV-2 variants
Abstract
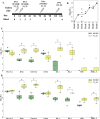
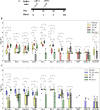
Updates of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are required to generate immunity in the population against constantly evolving SARS-CoV-2 variants of concerns (VOCs). Here we describe three novel in-silico designed spike-based antigens capable of inducing neutralising antibodies across a spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs. Three sets of antigens utilising pre-Delta (T2_32), and post-Gamma sequence data (T2_35 and T2_36) were designed. T2_32 elicited superior neutralising responses against VOCs compared to the Wuhan-1 spike antigen in DNA prime-boost immunisation regime in guinea pigs. Heterologous boosting with the attenuated poxvirus - Modified vaccinia Ankara expressing T2_32 induced broader neutralising immune responses in all primed animals. T2_32, T2_35 and T2_36 elicited broader neutralising capacity compared to the Omicron BA.1 spike antigen administered by mRNA immunisation in mice. These findings demonstrate the utility of structure-informed computationally derived modifications of spike-based antigens for inducing broad immune responses covering more than 2 years of evolved SARS-CoV-2 variants.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.K., R.W., and J.L.H. hold shares of DIOSynVax; R.K. is an employee of DIOSynVax. I.J and V.S are employees of ProBioGenAG, Berlin, Germany. J.G, C.D, V.M., A.R.S., C.P are employee of Ethris GmbH; Semmelweisstraße 3, 82152 Planegg, Germany. All other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Divergent SARS-CoV-2 variant emerges in white-tailed deer with deer-to-human transmission - PMC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9712111/. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

