NSD2 is a requisite subunit of the AR/FOXA1 neo-enhanceosome in promoting prostate tumorigenesis
- PMID: 39251788
- PMCID: PMC11525188
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01893-6
NSD2 is a requisite subunit of the AR/FOXA1 neo-enhanceosome in promoting prostate tumorigenesis
Abstract
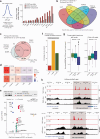
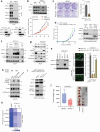
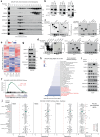
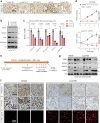
Androgen receptor (AR) is a ligand-responsive transcription factor that drives terminal differentiation of the prostatic luminal epithelia. By contrast, in tumors originating from these cells, AR chromatin occupancy is extensively reprogrammed to activate malignant phenotypes, the molecular mechanisms of which remain unknown. Here, we show that tumor-specific AR enhancers are critically reliant on H3K36 dimethyltransferase activity of NSD2. NSD2 expression is abnormally induced in prostate cancer, where its inactivation impairs AR transactivation potential by disrupting over 65% of its cistrome. NSD2-dependent AR sites distinctively harbor the chimeric FOXA1:AR half-motif, which exclusively comprise tumor-specific AR enhancer circuitries defined from patient specimens. NSD2 inactivation also engenders increased dependency on the NSD1 paralog, and a dual NSD1/2 PROTAC degrader is preferentially cytotoxic in AR-dependent prostate cancer models. Altogether, we characterize NSD2 as an essential AR neo-enhanceosome subunit that enables its oncogenic activity, and position NSD1/2 as viable co-targets in advanced prostate cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures











Update of
-
NSD2 is a requisite subunit of the AR/FOXA1 neo-enhanceosome in promoting prostate tumorigenesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 29:2024.02.22.581560. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.22.581560. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Genet. 2024 Oct;56(10):2132-2143. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01893-6. PMID: 38464251 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 CA187664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH-17-0404/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
- R00-CA187664/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- K00-CA245825/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- K00 CA245825/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA249210/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA186786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35-CA231996/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- U2C CA271854/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA231996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA249210-0/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH-21-1-0500/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA186786/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

