Association between urinary phthalate metabolites and Anemia in US adults
- PMID: 39251808
- PMCID: PMC11385222
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-72147-y
Association between urinary phthalate metabolites and Anemia in US adults
Abstract
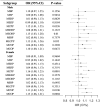
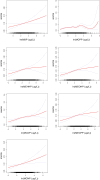
Initial research indicates a possible connection between exposure to phthalates and the development of anemia. To fill the gap in epidemiological data, our study utilized data from across the United States, representative on a national scale, to evaluate the association between the concentration of phthalate metabolites in urine and both anemia and iron levels. We gathered data on 11,406 individuals from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database, spanning 2003-2018. We conducted logistic and linear regression analyses, adjusted for potential confounding factors, to evaluate the correlations between different phthalate metabolites and anemia, as well as serum iron levels, including gender-stratified analysis. Most urinary phthalate metabolites were positively correlated with an increased risk of anemia, and the majority were negatively correlated with serum iron levels. The study revealed that for every unit increase in ln-transformed metabolite concentrations, the odds ratios (ORs) for anemia increased to varying degrees, depending on the phthalate: Monobutyl phthalate (MBP) at 1.08 (95% CI 1.01-1.17, P = 0.0314), mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (MCPP) at 1.17 (95% CI 1.10-1.24, P < 0.0001), mono(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP) at 1.08 (95% CI 1.02-1.15, P = 0.0153), mono(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate (MEOHP) at 1.14 (95% CI 1.07-1.21, P < 0.0001), mono(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate (MECPP) at 1.11 (95% CI 1.03-1.18, P = 0.0030), monocarboxynonyl phthalate (MCNP) at 1.11 (95% CI 1.03-1.19, p = 0.0050), and monocarboxyoctyl phthalate (MCOP) at 1.13 (95% CI 1.07-1.19, P < 0.0001). Increased levels of MBP, MEHP, MBzP, MCPP, MEHHP, MEOHP, MIBP, MECPP, MCNP, and MCOP were linked with changes in serum iron levels, ranging from - 0.99 µg/dL (95% CI - 1.69 to - 0.29) to - 3.72 µg/dL (95% CI - 4.32 to - 3.11). Mixed-exposure analysis shows consistency with single-exposure model. Further mediation analysis showed that the association between single urinary phthalates and the risk of anemia was mediated by serum iron with a mediation ratio of 24.34-95.48% (P < 0.05). The presence of phthalate metabolites in urine shows a positive correlation with the prevalence of anemia, which was possibly and partly mediated by iron metabolism. Nonetheless, to confirm a definitive causal link and comprehend the underlying mechanisms of how phthalate exposure influences anemia, additional longitudinal and experimental research is required.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Age and sex differences in childhood and adulthood obesity association with phthalates: analyses of NHANES 2007-2010.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2014 Jul;217(6):687-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2014.02.005. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2014. PMID: 24657244 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of urinary bisphenol A and phthalate metabolite concentrations in Mexican children.Chemosphere. 2013 Nov;93(10):2390-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.038. Epub 2013 Sep 14. Chemosphere. 2013. PMID: 24041567 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal urinary phthalate metabolites levels and neurodevelopment in children at two and three years of age.Sci Total Environ. 2013 Sep 1;461-462:386-90. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.021. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Sci Total Environ. 2013. PMID: 23747553 Free PMC article.
-
Phthalate exposure and risk of diabetes mellitus: Implications from a systematic review and meta-analysis.Environ Res. 2022 Mar;204(Pt B):112109. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112109. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 34562484
-
The Association of Bisphenol A and Phthalates with Risk of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 1;18(5):2375. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052375. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33804363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ezekowitz, J. A., McAlister, F. A. & Armstrong, P. W. Anemia is common in heart failure and is associated with poor outcomes: Insights from a cohort of 12 065 patients with new-onset heart failure. Circulation107, 223–225. 10.1161/01.cir.0000052622.51963.fc (2003). 10.1161/01.cir.0000052622.51963.fc - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

