Planting pattern and nitrogen management strategies: positive effect on yield and quality attributes of Triticum aestivum L. crop
- PMID: 39251892
- PMCID: PMC11382503
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05537-z
Planting pattern and nitrogen management strategies: positive effect on yield and quality attributes of Triticum aestivum L. crop
Abstract
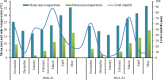
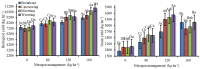
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a staple food crop that plays a crucial role in global food security. A suitable planting pattern and optimum nitrogen (N) split management are efficient practices for improving wheat production. Therefore, an experiment was performed to explore the effect of N split management and sowing patterns on wheat at the Agronomy Research Farm, The University of Agriculture Peshawar, during rabi season 2020-21 and 2021-22. The treatments consisted of different nitrogen rates of 0, 80, 120, and 160 kg ha- 1 and planting patterns of W, M, broadcast and line sowing. The pooled analysis of both cropping seasons showed that application of 120 kg N ha- 1 increased spikelets spike- 1, grains spike- 1, 1000 grains weight, grain yield, grain N content, evapotranspiration and water use efficiency by 21.9, 16.7, 21.8, 70, 13, 19.9 and 40% as compared to control, respectively. In addition, W and M were observed the best management practices among all planting patterns. The M planting pattern enhanced chlorophyll a, b, carotenoids and evapotranspiration while W plating pattern improved yield components and yield of wheat as compared to broadcast planting patterns. The principal component analysis biplot showed a close association of M and W planting patterns with 120 kg N ha- 1 in most of the studied traits. Hence, it is concluded that split application of 120 kg N ha- 1 in W and M sowing patterns enhanced growth, biochemical traits and water use efficiency, reducing N fertilization from 160 to 120 kg ha- 1 while increasing grain yield of wheat. Hence, it is recommended that application of 120 kg N ha⁻¹ in combination with W and M planting patterns offer a sustainable approach to enhancing wheat production in the alkaline soil conditions of the Peshawar valley.
Keywords: Evapotranspiration; Nitrogen management; Spatial arrangement; Water use efficiency.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- FAO. Statistical Yearbook. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2013. p. 289.
-
- Giraldo P, Benavente E, Manzano-Agugliaro F, Gimenez E. Worldwide research trends on wheat and barley: a bibliometric comparative analysis. Agronomy. 2019;9(7):352. 10.3390/agronomy9070352.10.3390/agronomy9070352 - DOI
-
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Retrieved from FAO website; 2021.
-
- Rahman M, Ali S, Khan M. Nitrogen management in wheat production. J Plant Nut Soil Sci. 2022;185(6):902–13. 10.1002/jpln.202200058.10.1002/jpln.202200058 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

