Rapid real-time quantitative colorimetric LAMP methodology for field detection of Verticillium dahliae in crude olive-plant samples
- PMID: 39252004
- PMCID: PMC11386372
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-024-01251-x
Rapid real-time quantitative colorimetric LAMP methodology for field detection of Verticillium dahliae in crude olive-plant samples
Abstract
Background: Verticilium dahliae is the most important wilt pathogen of olive trees with a broad host range causing devastating diseases currently without any effective chemical control. Traditional detection methodologies are based on symptoms-observation or lab-detection using time consuming culturing or molecular techniques. Therefore, there is an increasing need for portable tools that can detect rapidly V. dahliae in the field.
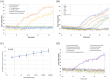
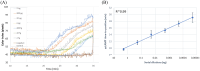
Results: In this work, we report the development of a novel method for the rapid, reliable and on-site detection of V. dahliae using a newly designed isothermal LAMP assay and crude extracts of olive wood. For the detection of the fungus, LAMP primers were designed targeting the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of the rRNA gene. The above assay was combined with a purpose-built prototype portable device which allowed real time quantitative colorimetric detection of V. dahliae in 35 min. The limit of detection of our assay was found to be 0.8 fg/μl reaction and the specificity 100% as indicated by zero cross-reactivity to common pathogens found in olive trees. Moreover, detection of V. dahliae in purified DNA gave a sensitivity of 100% (Ct < 30) and 80% (Ct > 30) while the detection of the fungus in unpurified crude wood extracts showed a sensitivity of 80% when multisampling was implemented. The superiority of the LAMP methodology regarding robustness and sensitivity was demonstrated when only LAMP was able to detect V. dahliae in crude samples from naturally infected trees with very low infection levels, while nested PCR and SYBR qPCR failed to detect the pathogen in an unpurified form.
Conclusions: This study describes the development of a new real time LAMP assay, targeting the ITS region of the rRNA gene of V. dahliae in olive trees combined with a 3D-printed portable device for field testing using a tablet. The assay is characterized by high sensitivity and specificity as well as ability to operate using directly crude samples such as woody tissue or petioles. The reported methodology is setting the basis for the development of an on-site detection methodology for V. dahliae in olive trees, but also for other plant pathogens.
Keywords: Verticillium wilt; Defoliating pathotype; Field-based detection; Loop mediated isothermal amplification; Molecular diagnostics; Soilborne pathogens.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr G. Papadakis and Prof E. Gizeli are co-founders of BIOPIX DNA TECHNOLOGY, a spin-off of IMBB-FORTH that commercializes the prototype device shown in this work. The other authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel and rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the specific detection of Verticillium dahliae.J Appl Microbiol. 2014 Apr;116(4):942-54. doi: 10.1111/jam.12407. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J Appl Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24329885
-
Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Verticillium dahliae from Soil Using LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a Technology.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 10;25(10):5185. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105185. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791224 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of real-time PCR protocols for the quantitative monitoring of asymptomatic olive infections by Verticillium dahliae pathotypes.Phytopathology. 2013 Oct;103(10):1058-68. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-11-12-0312-R. Phytopathology. 2013. PMID: 23777403
-
Verticillium Wilt of Olive and its Control: What Did We Learn during the Last Decade?Plants (Basel). 2020 Jun 11;9(6):735. doi: 10.3390/plants9060735. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of the Molecular Genetics of Plant Resistance to the Verticillium Wilt Pathogen Verticillium dahliae.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 7;21(3):1120. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031120. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32046212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LAMP Reaction in Plant Disease Surveillance: Applications, Challenges, and Future Perspectives.Life (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;14(12):1549. doi: 10.3390/life14121549. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768257 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amoia SS, Loconsole G, Ligorio A, et al. A colorimetric LAMP detection of Xylella fastidiosa in crude alkaline sap of olive trees in apulia as a field-based tool for disease containment. Agriculture (Switzerland). 2023;13:448.
-
- Aslani S, Garoosi G, Jafary H. Using a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay and direct DNA extraction method from wood for rapid detection of Verticillium dahliae in olive trees. Biosci, Biotechnol Res Asia. 2017;14:727–34.10.13005/bbra/2501 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

