Safety and efficacy of S1P receptor modulators for the induction and maintenance phases in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 39252283
- PMCID: PMC11383267
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039372
Safety and efficacy of S1P receptor modulators for the induction and maintenance phases in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory condition that significantly affects quality of life. Conventional treatments have had limited success. this study evaluates the safety and efficacy of Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators (S1PrMs) as a potential treatment for IBD.
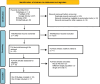
Methods: We conducted a thorough search of published literature on PubMed, EMBASE, and Google Scholar from 2000 to 2023. The inclusion criteria were randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with a target population comprising of IBD patients receiving either S1PrMs or placebo and a comparison of the 2. The statistical analysis was conducted using RevMan (version 5.4). Forest plots presented the results as risk ratios (RR) with a 95% confidence interval.
Results: A total of 7 RCTs involving 2471 patients were included. The results were reported for both the induction and maintenance phases of treatment. in the induction phase, the intervention group proved to have a significantly higher incidence of histological remission (RR = 2.67; 95% CI [1.97, 3.60]; P < .00001), endoscopic improvement (RR = 2.06; 95% CI [1.66, 2.56]; P < .00001), clinical remission (RR = 2.23; 95% CI [1.43, 3.46]; P < .0004) and clinical response (RR = 1.37; 95% CI [1.01, 1.84]; P = .04) compared to the placebo group. Outcomes assessed in maintenance phase significantly favored the intervention group over placebo as well, histologic remission (RR = 2.39; 95% CI [1.83, 3.11]; P < .00001), endoscopic improvement (RR = 2.20; 95% CI [1.28, 3.77]; P = .004), clinical remission (RR = 3.03; 95% CI [1.84, 4.99]; P < .0001), and clinical response (RR = 1.74; 95% CI [1.25, 2.42]; P = .001).
Conclusion: S1PrMs show promising potential for establishing histologic remission, endoscopic improvement, clinical remission, and corticosteroid-free clinical remission. With more studies and clinical trials, these modulators may become a reliable therapeutic choice for UC patients everywhere.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Rubin DT, Ananthakrishnan AN, Siegel CA, Sauer BG, Long MD. ACG clinical guideline: ulcerative colitis in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114:384–413. - PubMed
-
- Porro GB, Cassinotti A, Ferrara E, Maconi G, Ardizzone S. The management of steroid dependency in ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26:779–94. - PubMed
-
- Gordon JP, McEwan PC, Maguire A, Sugrue DM, Puelles J. Characterizing unmet medical need and the potential role of new biologic treatment options in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease: a systematic review and clinician surveys. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;27:804–12. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
