Radiogenomics: bridging the gap between imaging and genomics for precision oncology
- PMID: 39252824
- PMCID: PMC11381657
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.722
Radiogenomics: bridging the gap between imaging and genomics for precision oncology
Abstract
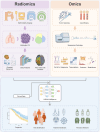
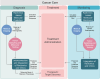
Genomics allows the tracing of origin and evolution of cancer at molecular scale and underpin modern cancer diagnosis and treatment systems. Yet, molecular biomarker-guided clinical decision-making encounters major challenges in the realm of individualized medicine, consisting of the invasiveness of procedures and the sampling errors due to high tumor heterogeneity. By contrast, medical imaging enables noninvasive and global characterization of tumors at a low cost. In recent years, radiomics has overcomes the limitations of human visual evaluation by high-throughput quantitative analysis, enabling the comprehensive utilization of the vast amount of information underlying radiological images. The cross-scale integration of radiomics and genomics (hereafter radiogenomics) has the enormous potential to enhance cancer decoding and act as a catalyst for digital precision medicine. Herein, we provide a comprehensive overview of the current framework and potential clinical applications of radiogenomics in patient care. We also highlight recent research advances to illustrate how radiogenomics can address common clinical problems in solid tumors such as breast cancer, lung cancer, and glioma. Finally, we analyze existing literature to outline challenges and propose solutions, while also identifying future research pathways. We believe that the perspectives shared in this survey will provide a valuable guide for researchers in the realm of radiogenomics aiming to advance precision oncology.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; oncology; precision medicine; radiogenomics; radiomics.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From Images to Genes: Radiogenomics Based on Artificial Intelligence to Achieve Non-Invasive Precision Medicine in Cancer Patients.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(2):e2408069. doi: 10.1002/advs.202408069. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39535476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomics and radiogenomics for precision radiotherapy.J Radiat Res. 2018 Mar 1;59(suppl_1):i25-i31. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrx102. J Radiat Res. 2018. PMID: 29385618 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Radiogenomics for Cancers in the Era of Precision Medicine.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 9;14(12):2860. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122860. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiogenomics in prostate cancer evaluation.Curr Opin Urol. 2021 Jul 1;31(4):424-429. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000000902. Curr Opin Urol. 2021. PMID: 34009176 Review.
-
Radiomics and radiogenomics: extracting more information from medical images for the diagnosis and prognostic prediction of ovarian cancer.Mil Med Res. 2024 Dec 14;11(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00580-1. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39673071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision Targeting in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Molecular Insights to Therapeutic Frontiers.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 27;15(5):625. doi: 10.3390/biom15050625. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measured intrapatient radiomic variability as a predictor of treatment response in multi-metastatic soft tissue sarcoma patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 30;15(1):27838. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12451-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40739225 Free PMC article.
-
Measured intrapatient radiomic variability as a predictor of treatment response in multi-metastatic soft tissue sarcoma patients.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 14:2025.04.11.25325700. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.11.25325700. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 30;15(1):27838. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12451-3. PMID: 40297462 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Integrating Radiogenomics and Machine Learning in Musculoskeletal Oncology Care.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 29;15(11):1377. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111377. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40506947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209‐249. - PubMed
-
- De Visser KE, Joyce JA. The evolving tumor microenvironment: from cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell. 2023;41(3):374‐403. - PubMed
-
- Akhoundova D, Rubin MA. Clinical application of advanced multi‐omics tumor profiling: shaping precision oncology of the future. Cancer Cell. 2022;40(9):920‐938. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
