From immune dysregulation to organ dysfunction: understanding the enigma of Sepsis
- PMID: 39252831
- PMCID: PMC11381394
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1415274
From immune dysregulation to organ dysfunction: understanding the enigma of Sepsis
Abstract
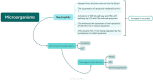
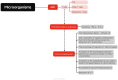
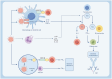
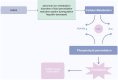
Sepsis is a syndrome precipitated by immune dysregulation in response to infection, and represents a pivotal factor in global mortality attributed to diseases. The recent consensus delineates sepsis as a perilous state of organ dysfunction arising from the host's maladaptive reaction to infection. It masks the complexity and breadth of the immune mechanisms involved in sepsis, which is characterized by simultaneous hyperinflammation and immunosuppression. Sepsis is highly correlated with the dysregulation of immune response, which is mainly mediated by various immune cells and their interactions. This syndrome can lead to a plethora of complications, encompassing systemic inflammatory response, metabolic disturbances, infectious shock, MODS, and DIC. Furthermore, more research studies have been conducted on sepsis in the past few years. The pathological characteristics of sepsis have been improved or treated by targeting signaling pathways like NF-B, JAK-STAT, PI3K-Akt, and p38-MAPK. Combined drug therapy is better than single drug therapy for sepsis. This article will review the latest progress in the pathogenesis and treatment of sepsis.
Keywords: Sepsis; T cells; cytokines; molecular mechanism; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Ting, Li, Li, Tan and Long.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- An Y. Z. (2009). Vascular endothelial injury: a key event in occurrence and development of sepsis-relationship of treatment and life-saving in critical medicine. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 89, 2737–2738., PMID: - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

