This is a preprint.
Open Access Data Repository and Common Data Model for Pulse Oximeter Performance Data
- PMID: 39252896
- PMCID: PMC11383449
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.08.30.24312744
Open Access Data Repository and Common Data Model for Pulse Oximeter Performance Data
Update in
-
Open Access Dataset and Common Data Model for Pulse Oximeter Performance Data.Sci Data. 2025 Apr 3;12(1):570. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04870-8. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40180919 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The OpenOximetry Repository is a structured database storing clinical and lab pulse oximetry data, serving as a centralized repository and data model for pulse oximetry initiatives. It supports measurements of arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) by arterial blood gas co-oximetry and pulse oximetry (SpO2), alongside processed and unprocessed photoplethysmography (PPG) data and other metadata. This includes skin color measurements, finger diameter, vital signs (e.g., arterial blood pressure, end-tidal carbon dioxide), and arterial blood gas parameters (e.g., acid-base balance, hemoglobin concentration). Data contributions are encouraged. All data, from desaturation studies to clinical trials, are collected prospectively to ensure accuracy. A common data model and standardized protocols for consistent archival and interpretation ensure consistent data archival and interpretation. The dataset aims to facilitate research on pulse oximeter performance across diverse human characteristics, addressing performance issues and promoting accurate pulse oximeters. The initial release includes controlled lab desaturation studies (CLDS), with ongoing updates planned as further data from clinical trials and CLDS become available.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests The UCSF Hypoxia Research Laboratory receives funding from pulse oximeter manufacturers/sponsors to test the sponsors’ devices for the purposes of product development and regulatory performance testing. Data submitted by the UCSF Hypoxia Lab for this repository do not include Hypoxia Lab sponsors’ study devices unless the sponsor provides consent to include these data. Otherwise, all UCSF Hypoxia Lab data are collected from devices procured by the Hypoxia Lab for the purposes of independent research. At the time of this publication, no pulse oximeter company provides direct funding for the Open Oximetry Project, participates in study design or analysis, or is involved in the creation of this data repository. None of the investigators who maintain this database own stock or equity interests in any pulse oximeter device companies. AIW holds equity and management roles in Ataia Medical. Atia Medical was not involved in study design, funding, or any portion of the study. There are no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
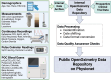
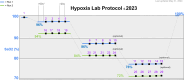
References
-
- Feiner J. R., Severinghaus J. W. & Bickler P. E. Dark skin decreases the accuracy of pulse oximeters at low oxygen saturation: the effects of oximeter probe type and gender. Anesth. Analg. 105, S18–S23 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Bickler P. E., Feiner J. R. & Severinghaus J. W. Effects of skin pigmentation on pulse oximeter accuracy at low saturation. Anesthesiology 102, 715–719 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Emery J. R. Skin pigmentation as an influence on the accuracy of pulse oximetry. J. Perinatol. Off. J. Calif. Perinat. Assoc. 7, 329–330 (1987). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
