Optic nerve sheath diameters in nontraumatic brain injury: A scoping review and role in the intensive care unit
- PMID: 39253313
- PMCID: PMC11372515
- DOI: 10.5492/wjccm.v13.i3.97205
Optic nerve sheath diameters in nontraumatic brain injury: A scoping review and role in the intensive care unit
Abstract
Background: Neuromonitoring in medical intensive care units is challenging as most patients are unfit for invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) modalities or unstable to transport for imaging. Ultrasonography-based optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) is an attractive option as it is reliable, repeatable and easily performed at the bedside. It has been sufficiently validated in traumatic brain injury (TBI) to be incorporated into the guidelines. However, currently the data for non-TBI patients is inconsistent for a scientific recommendation to be made.
Aim: To compile the existing evidence for understanding the scope of ONSD in measuring ICP in adult non-traumatic neuro-critical patients.
Methods: PubMed, Google Scholar and research citation analysis databases were searched for studies in adult patients with non-traumatic causes of raised ICP. Studies from 2010 to 2024 in English languages were included.
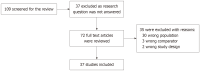
Results: We found 37 articles relevant to our search. The cutoff for ONSD in predicting ICP varied from 4.1 to 6.3 mm. Most of the articles used cerebrospinal fluid opening pressure followed by raised ICP on computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging as the comparator parameter. ONSD was also found to be a reliable outcome measure in cases of acute ischaemic stroke, intracerebral bleeding and intracranial infection. However, ONSD is of doubtful utility in septic metabolic encephalopathy, dysnatremias and aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage.
Conclusion: ONSD is a useful tool for the diagnosis of raised ICP in non-traumatic neuro-critically ill patients and may also have a role in the prognostication of a subset of patients.
Keywords: Intracranial hypertension; Intracranial pressure monitoring; Medical intensive care unit; Neuro-monitoring; Non-traumatic brain injury; Optic nerve sheath diameter; Optic nerve ultrasound.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors affirm that they have no conflicts of interest pertaining to the subject matter discussed in this paper.
Similar articles
-
Using Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter for Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Scoping Review.Neurocrit Care. 2024 Jun;40(3):1193-1212. doi: 10.1007/s12028-023-01884-1. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Neurocrit Care. 2024. PMID: 38114797 Free PMC article.
-
Bedside ultrasonography of optic nerve sheath diameter for detection of raised intracranial pressure in nontraumatic neuro-critically ill patients.World J Crit Care Med. 2023 Jan 9;12(1):10-17. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v12.i1.10. eCollection 2023 Jan 9. World J Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36683966 Free PMC article.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter measurement: a means of detecting raised ICP in adult traumatic and non-traumatic neurosurgical patients.Am J Emerg Med. 2017 Jan;35(1):150-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.09.044. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Am J Emerg Med. 2017. PMID: 27852525
-
Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter is not Related to Intracranial Pressure in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients.Neurocrit Care. 2020 Oct;33(2):491-498. doi: 10.1007/s12028-020-00970-y. Neurocrit Care. 2020. PMID: 32314244
-
The role of optic nerve sheath diameter ultrasound in brain infection.eNeurologicalSci. 2021 Feb 22;23:100330. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2021.100330. eCollection 2021 Jun. eNeurologicalSci. 2021. PMID: 33728383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ohle R, McIsaac SM, Woo MY, Perry JJ. Sonography of the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter for Detection of Raised Intracranial Pressure Compared to Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34:1285–1294. - PubMed
-
- Tayal VS, Neulander M, Norton HJ, Foster T, Saunders T, Blaivas M. Emergency department sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter to detect findings of increased intracranial pressure in adult head injury patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49:508–514. - PubMed
-
- Ballantyne SA, O'Neill G, Hamilton R, Hollman AS. Observer variation in the sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter in normal adults. Eur J Ultrasound. 2002;15:145–149. - PubMed
-
- Carney N, Totten AM, O'Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ, Bratton SL, Chesnut R, Harris OA, Kissoon N, Rubiano AM, Shutter L, Tasker RC, Vavilala MS, Wilberger J, Wright DW, Ghajar J. Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery. 2017;80:6–15. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources