This is a preprint.
Programmable scanning diffuse speckle contrast imaging of cerebral blood flow
- PMID: 39253639
- PMCID: PMC11383439
Programmable scanning diffuse speckle contrast imaging of cerebral blood flow
Update in
-
Programmable scanning diffuse speckle contrast imaging of cerebral blood flow.Neurophotonics. 2025 Jan;12(1):015006. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.12.1.015006. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Neurophotonics. 2025. PMID: 39872020 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Significance: Cerebral blood flow (CBF) imaging is crucial for diagnosing cerebrovascular diseases. However, existing large neuroimaging techniques with high cost, low sampling rate, and poor mobility make them unsuitable for continuous and longitudinal CBF monitoring at the bedside.
Aim: This study aimed to develop a low-cost, portable, programmable scanning diffuse speckle contrast imaging (PS-DSCI) technology for fast, high-density, and depth-sensitive imaging of CBF in rodents.
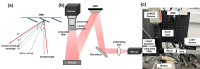
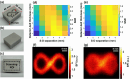
Approach: The PS-DSCI employed a programmable digital micromirror device (DMD) for remote line-shape laser (785 nm) scanning on tissue surface and synchronized a 2D camera for capturing boundary diffuse laser speckle contrasts. New algorithms were developed to address deformations of line-shape scanning, thus minimizing CBF reconstruction artifacts. The PS-DSCI was examined in head-simulating phantoms and adult mice.
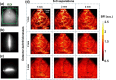
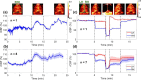
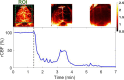
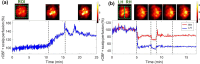
Results: The PS-DSCI enables resolving Intralipid particle flow contrasts at different tissue depths. In vivo experiments in adult mice demonstrated the capability of PS-DSCI to image global/regional CBF variations induced by 8% CO2 inhalation and transient carotid artery ligations.
Conclusions: Compared to conventional point scanning, the line scanning in PS-DSCI significantly increases spatiotemporal resolution. The high sampling rate of PS-DSCI is crucial for capturing rapid CBF changes while high spatial resolution is important for visualizing brain vasculature.
Keywords: cerebral blood flow; diffuse optics; digital micromirror device; line-shape scanning; speckle contrast imaging.
Figures


References
-
- Bandera E., et al. , Cerebral blood flow threshold of ischemic penumbra and infarct core in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Stroke, 2006. 37(5): p. 1334–1339. - PubMed
-
- Yonas H., et al. , Increased stroke risk predicted by compromised cerebral blood flow reactivity. Journal of neurosurgery, 1993. 79(4): p. 483–489. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
