Mitochondrial reprogramming by activating OXPHOS via glutamine metabolism in African American patients with bladder cancer
- PMID: 39253977
- PMCID: PMC11385078
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.172336
Mitochondrial reprogramming by activating OXPHOS via glutamine metabolism in African American patients with bladder cancer
Abstract
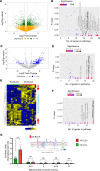
Bladder cancer (BLCA) mortality is higher in African American (AA) patients compared with European American (EA) patients, but the molecular mechanism underlying race-specific differences are unknown. To address this gap, we conducted comprehensive RNA-Seq, proteomics, and metabolomics analysis of BLCA tumors from AA and EA. Our findings reveal a distinct metabolic phenotype in AA BLCA characterized by elevated mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), particularly through the activation of complex I. The results provide insight into the complex I activation-driven higher OXPHOS activity resulting in glutamine-mediated metabolic rewiring and increased disease progression, which was also confirmed by [U]13C-glutamine tracing. Mechanistic studies further demonstrate that knockdown of NDUFB8, one of the components of complex I in AA BLCA cells, resulted in reduced basal respiration, ATP production, GLS1 expression, and proliferation. Moreover, preclinical studies demonstrate the therapeutic potential of targeting complex I, as evidenced by decreased tumor growth in NDUFB8-depleted AA BLCA tumors. Additionally, genetic and pharmacological inhibition of GLS1 attenuated mitochondrial respiration rates and tumor growth potential in AA BLCA. Taken together, these findings provide insight into BLCA disparity for targeting GLS1-Complex I for future therapy.
Keywords: Cancer; Metabolism; Mitochondria; Oncology; Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 CA289419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA282282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA220297/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 CA284971/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA253445/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES027725/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA142543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA216426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114356/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA239755/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES030285/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 CA284967/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA254988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006348/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028648/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130249/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

