Exploring the Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease: An Educational Literature Review
- PMID: 39254911
- PMCID: PMC12078384
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-024-04468-y
Exploring the Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease: An Educational Literature Review
Abstract
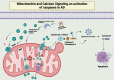
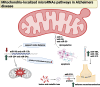
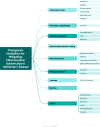
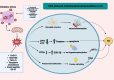
Alzheimer's disease (AD) presents a significant challenge to global health. It is characterized by progressive cognitive deterioration and increased rates of morbidity and mortality among older adults. Among the various pathophysiologies of AD, mitochondrial dysfunction, encompassing conditions such as increased reactive oxygen production, dysregulated calcium homeostasis, and impaired mitochondrial dynamics, plays a pivotal role. This review comprehensively investigates the mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction in AD, focusing on aspects such as glucose metabolism impairment, mitochondrial bioenergetics, calcium signaling, protein tau and amyloid-beta-associated synapse dysfunction, mitophagy, aging, inflammation, mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria-localized microRNAs, genetics, hormones, and the electron transport chain and Krebs cycle. While lecanemab is the only FDA-approved medication to treat AD, we explore various therapeutic modalities for mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction in AD, including antioxidant drugs, antidiabetic agents, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (FDA-approved to manage symptoms), nutritional supplements, natural products, phenylpropanoids, vaccines, exercise, and other potential treatments.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease; Mitochondrial Dysfunction; Therapeutic Modalities.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Approval: Not applicable, and all data are available on the internet. Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alkon D, Sun MK, Thompson R (2021) Evidence of significant cognitive improvement over baseline in advanced Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients: a regenerative therapeutic strategy. Alzheimers Dement 17(S9):e050013
-
- Kashif M, Sivaprakasam P, Vijendra P, Waseem M, Pandurangan AK (2023) A recent update on pathophysiology and therapeutic interventions of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des. 10.2174/0113816128264355231121064704 - PubMed
-
- Gettman L (2024) Lecanemab-irmb (Leqembi™) for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Sr Care Pharm 39(2):75–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

