Male cuticular pheromones stimulate removal of the mating plug and promote re-mating through pC1 neurons in Drosophila females
- PMID: 39255004
- PMCID: PMC11386958
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.96013
Male cuticular pheromones stimulate removal of the mating plug and promote re-mating through pC1 neurons in Drosophila females
Abstract
In birds and insects, the female uptakes sperm for a specific duration post-copulation known as the ejaculate holding period (EHP) before expelling unused sperm and the mating plug through sperm ejection. In this study, we found that Drosophila melanogaster females shortens the EHP when incubated with males or mated females shortly after the first mating. This phenomenon, which we termed
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Or47b; mating; neuroscience; pC1; ppk23; sexual plasticity; sperm ejection.
© 2024, Yun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MY, DK, TH, KL, EP, MK, BH, YK No competing interests declared
Figures

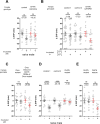
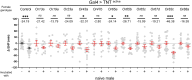
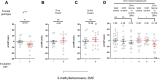
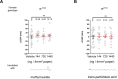


Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.11.28.568981
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96013.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96013.2
Similar articles
-
Pheromones mediating copulation and attraction in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 26;112(21):E2829-35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504527112. Epub 2015 May 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25964351 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila pheromone-sensing neurons expressing the ppk25 ion channel subunit stimulate male courtship and female receptivity.PLoS Genet. 2014 Mar 27;10(3):e1004238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004238. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24675786 Free PMC article.
-
Retention of Ejaculate by Drosophila melanogaster Females Requires the Male-Derived Mating Plug Protein PEBme.Genetics. 2015 Aug;200(4):1171-9. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.176669. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26058847 Free PMC article.
-
Mating induces developmental changes in the insect female reproductive tract.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2016 Feb;13:106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2016. PMID: 27436559 Review.
-
Chemical Cues that Guide Female Reproduction in Drosophila melanogaster.J Chem Ecol. 2018 Sep;44(9):750-769. doi: 10.1007/s10886-018-0947-z. Epub 2018 Mar 19. J Chem Ecol. 2018. PMID: 29557077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Becker SD, Hurst JL. In: Chemical Signals in Vertebrates 11. Hurst JL, Beynon RJ, Roberts SC, Wyatt TD, editors. New York, NY: Springer; 2008. Pregnancy block from a female perspective in; pp. 141–150. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NRF-2022M3H9A1085169/National Research Foundation of Korea
- P40 OD018537/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- NRF-2021R1I1A1A01060304/National Research Foundation of Korea
- AI-based GIST Research Scientist Project/Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
- NRF-2022R1A2C3008091/National Research Foundation of Korea
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

