Correlates of Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women attending antenatal clinics in Wa Municipality, Ghana
- PMID: 39255265
- PMCID: PMC11386425
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002447
Correlates of Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women attending antenatal clinics in Wa Municipality, Ghana
Abstract
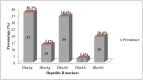
Despite the availability of an effective vaccine against viral hepatitis B infection, it remains prevalent, highly transmissible especially through mother-to-child, life-threatening, and a major public health challenge. A positive Hepatitis B e-Antigen (HBeAg) mother has a 90% risk of transmitting the virus to the unborn child in the perinatal period. This study sought to determine the prevalence and risk of Hepatitis B infection among pregnant women in the Wa Municipality of Ghana. A cross-sectional study employing systematic random sampling was conducted among 183 consented pregnant women who went for antenatal care in nine health facilities in the Wa Municipality. A structured validated questionnaire was used to collect information about socio-demographic and obstetric characteristics, awareness of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) transmission and its prevention. Blood samples (3.0 mls) were collected from each participant to test for HBV serum markers using a Wondfo One Step HBV rapid immunochromatographic assay (Catalog number W003) for the Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). We conducted descriptive statistics including the prevalence and used multivariable logistic regression to determine the risk of Hepatitis B among study participants. Data was analysed using Stata/SE 15. About 20.2% of the 183 pregnant women screened tested positive for HBsAg. Generally, compared with younger pregnant women, older (> = 25) pregnant women were >9 times less likely to test positive for both chronic Hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb) and (HBeAg) Hepatitis B infections. However, pregnant women in polygamous relationship were more likely to test positive for both (HBcAb) and (HBsAg and HBeAg) Hepatitis B infections compared with those in monogamous relationship. In a multivariable analysis, pregnant women in a polygamous relationships were about 5 times more likely to test positive for HBsAg (AOR = 4.61, 95% CI: 2.06-9.89) and HBcAb (AOR = 4.89, 95% CI:1.52-6.81) and HBeAg (AOR = 4.62, 95% CI:1.21-6.39) compared with those in a monogamous relationship. This study highlights a high HBsAg prevalence among pregnant women with those in polygamous relationship and younger age more likely to test positive. Facility and community-based health services should emphasize the need for regular screening, education, and vaccination of pregnant women, especially those at high risk, to prevent mother-to-child transmission of viral hepatitis B.
Copyright: © 2024 Awiah et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, Hepatitis B Key Facts. 2024.
-
- Coalition for Global Hepatitis Elimination, Ghana can eliminate Hepatitis: National Hepatitis elimination profile 2022.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources