PP1 phosphatase controls both daughter cell formation and amylopectin levels in Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 39255306
- PMCID: PMC11414933
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002791
PP1 phosphatase controls both daughter cell formation and amylopectin levels in Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
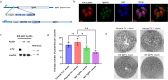
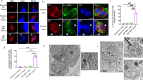
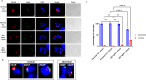
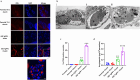
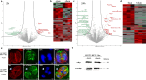
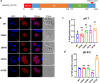
Virulence of apicomplexan parasites is based on their ability to divide rapidly to produce significant biomass. The regulation of their cell cycle is therefore key to their pathogenesis. Phosphorylation is a crucial posttranslational modification that regulates many aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. The phosphatase PP1 is known to play a major role in the phosphorylation balance in eukaryotes. We explored the role of TgPP1 during the cell cycle of the tachyzoite form of the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Using a conditional mutant strain, we show that TgPP1 regulates many aspects of the cell cycle including the proper assembly of the daughter cells' inner membrane complex (IMC), the segregation of organelles, and nuclear division. Unexpectedly, depletion of TgPP1 also results in the accumulation of amylopectin, a storage polysaccharide that is usually found in the latent bradyzoite form of the parasite. Using transcriptomics and phospho-proteomics, we show that TgPP1 mainly acts through posttranslational mechanisms by dephosphorylating target proteins including IMC proteins. TgPP1 also dephosphorylates a protein bearing a starch-binding domain. Mutagenesis analysis reveals that the targeted phospho-sites are linked to the ability of the parasite to regulate amylopectin steady-state levels. Therefore, we show that TgPP1 has pleiotropic roles during the tachyzoite cell cycle regulation, but also regulates amylopectin accumulation.
Copyright: © 2024 Khelifa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma gondii Requires Glycogen Phosphorylase for Balancing Amylopectin Storage and for Efficient Production of Brain Cysts.mBio. 2017 Aug 29;8(4):e01289-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01289-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28851850 Free PMC article.
-
Cascading expression of ApiAP2 transcription factors controls daughter cell assembly in Toxoplasma gondii.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Dec 30;20(12):e1012810. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012810. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39774584 Free PMC article.
-
The Toxoplasma gondii inhibitor-2 regulates protein phosphatase 1 activity through multiple motifs.Parasitol Res. 2017 Sep;116(9):2417-2426. doi: 10.1007/s00436-017-5543-6. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Parasitol Res. 2017. PMID: 28667522
-
Developmentally regulated biosynthesis of carbohydrate and storage polysaccharide during differentiation and tissue cyst formation in Toxoplasma gondii.Biochimie. 2003 Mar-Apr;85(3-4):353-61. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(03)00076-2. Biochimie. 2003. PMID: 12770773 Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Hsp90: potential roles in essential cellular processes of the parasite.Parasitology. 2014 Aug;141(9):1138-47. doi: 10.1017/S0031182014000055. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Parasitology. 2014. PMID: 24560345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

