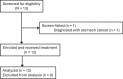
Interim safety and efficacy of gene therapy for RLBP1-associated retinal dystrophy: a phase 1/2 trial
- PMID: 39256350
- PMCID: PMC11387776
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51575-4
Interim safety and efficacy of gene therapy for RLBP1-associated retinal dystrophy: a phase 1/2 trial
Abstract
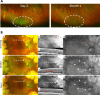
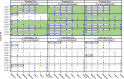
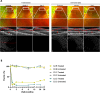
Gene therapy holds promise for treatment of inherited retinal dystrophies, a group of rare genetic disorders characterized by severe loss of vision. Here, we report up to 3-year pre-specified interim safety and efficacy results of an open-label first-in-human dose-escalation phase 1/2 gene therapy clinical trial in 12 patients with retinal dystrophy caused by biallelic mutations in the retinaldehyde-binding protein 1 (RLBP1) gene of the visual cycle. The primary endpoints were systemic and ocular safety and recovery of dark adaptation. Secondary endpoints included microperimetry, visual field sensitivity, dominant eye test and patient-reported outcomes. Subretinal delivery of an adeno-associated viral vector (AAV8-RLBP1) was well tolerated with dose-dependent intraocular inflammation which responded to corticosteroid treatment, and focal atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium as the dose limiting toxicity. Dark adaptation kinetics, the primary efficacy endpoint, improved significantly in all dose-cohorts. Treatment with AAV8-RLBP1 resulted in the resolution of disease-related retinal deposits, suggestive of successful restoration of the visual cycle. In conclusion, to date, AAV8-RLBP1 has shown preliminary safety and efficacy in patients with RLBP1-associated retinal dystrophy. Trial number: NCT03374657.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.R., K.H., C.W., N.J., C.B., K.S., M.L., and C.G. were employees of the sponsor of the trial, Novartis Pharma AG. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Morimura, H., Berson, E. L. & Dryja, T. P. Recessive mutations in the RLBP1 gene encoding cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein in a form of retinitis punctata albescens. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.40, 1000–1004 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

