LOXHD1 is indispensable for maintaining TMC1 auditory mechanosensitive channels at the site of force transmission
- PMID: 39256406
- PMCID: PMC11387651
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51850-4
LOXHD1 is indispensable for maintaining TMC1 auditory mechanosensitive channels at the site of force transmission
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: LOXHD1 is indispensable for maintaining TMC1 auditory mechanosensitive channels at the site of force transmission.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 15;15(1):8878. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52972-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39406713 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
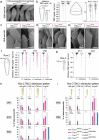
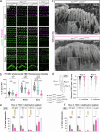
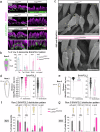
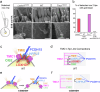
Hair cell bundles consist of stereocilia arranged in rows of increasing heights, connected by tip links that transmit sound-induced forces to shorter stereocilia tips. Auditory mechanotransduction channel complexes, composed of proteins TMC1/2, TMIE, CIB2, and LHFPL5, are located at the tips of shorter stereocilia. While most components can interact with the tip link in vitro, their ability to maintain the channel complexes at the tip link in vivo is uncertain. Return, using mouse models, we show that an additional component, LOXHD1, is essential for keeping TMC1-pore forming subunits at the tip link but is dispensable for TMC2. Using SUB-immunogold-SEM, we showed that TMC1 localizes near the tip link but mislocalizes without LOXHD1. LOXHD1 selectively interacts with TMC1, CIB2, LHFPL5, and tip-link protein PCDH15. Our results demonstrate that TMC1-driven mature auditory channels require LOXHD1 to stay connected to the tip link and remain functional, while TMC2-driven developmental channels do not.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Update of
-
LOXHD1 is indispensable for coupling auditory mechanosensitive channels to the site of force transmission.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 2:rs.3.rs-3752492. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3752492/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 10;15(1):7865. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51850-4. PMID: 38260480 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 AG081608/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01DC016409-01A1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
- 1R01DC021835-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
- R01 DC021835/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC016409/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG081608-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- R21 DC019457/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DC019195/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R21DC019195/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

