Digital speech hearing screening using a quick novel mobile hearing impairment assessment: an observational correlation study
- PMID: 39256446
- PMCID: PMC11387469
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67539-z
Digital speech hearing screening using a quick novel mobile hearing impairment assessment: an observational correlation study
Abstract
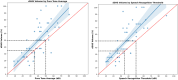
By 2050, 1 in 4 people worldwide will be living with hearing impairment. We propose a digital Speech Hearing Screener (dSHS) using short nonsense word recognition to measure speech-hearing ability. The importance of hearing screening is increasing due to the anticipated increase in individuals with hearing impairment globally. We compare dSHS outcomes with standardized pure-tone averages (PTA) and speech-recognition thresholds (SRT). Fifty participants (aged 55 or older underwent pure-tone and speech-recognition thresholding. One-way ANOVA was used to compare differences between hearing impaired and hearing not-impaired groups, by the dSHS, with a clinical threshold of moderately impaired hearing at 35 dB and severe hearing impairment at 50 dB. dSHS results significantly correlated with PTAs/SRTs. ANOVA results revealed the dSHS was significantly different (F(1,47) = 38.1, p < 0.001) between hearing impaired and unimpaired groups. Classification analysis using a 35 dB threshold, yielded accuracy of 85.7% for PTA-based impairment and 81.6% for SRT-based impairment. At a 50 dB threshold, dSHS classification accuracy was 79.6% for PTA-based impairment (Negative Predictive Value (NPV)-93%) and 83.7% (NPV-100%) for SRT-based impairment. The dSHS successfully differentiates between hearing-impaired and unimpaired individuals in under 3 min. This hearing screener offers a time-saving, in-clinic hearing screening to streamline the triage of those with likely hearing impairment to the appropriate follow-up assessment, thereby improving the quality of services. Future work will investigate the ability of the dSHS to help rule out hearing impairment as a cause or confounder in clinical and research applications.
Keywords: Cognition; Digital hearing screening; Pure tone audiometry; Speech recognition.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DB is a co-founder of Linus Health and declares ownership of shares or share options in the company. RB, BG, IM, MC, JGO, AJ, ST, and JS are employees of Linus Health and declare ownership of shares or share options in the company. Author DW does not have any competing interests to declare. APL is a co-founder of Linus Health and TI Solutions and declares ownership of shares or share options in the company. APL serves as a paid member of the scientific advisory boards for Neuroelectrics, Magstim Inc., TetraNeuron, Skin2Neuron, MedRhythms, and Hearts Radiant, and is listed as an inventor on several issued and pending patents on the real-time integration of transcranial magnetic stimulation with electroencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging, applications of noninvasive brain stimulation in various neurological disorders, as well as digital biomarkers of cognition and digital assessments for early diagnosis of dementia.
Figures




Similar articles
-
School-Age Hearing Screening Based on Speech-in-Noise Perception Using the Digit Triplet Test.Ear Hear. 2018 Nov/Dec;39(6):1104-1115. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000563. Ear Hear. 2018. PMID: 29557793
-
Identifying Subclinical Hearing Loss: Extended Audiometry and Word Recognition in Noise.Audiol Neurootol. 2022;27(3):217-226. doi: 10.1159/000518962. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Audiol Neurootol. 2022. PMID: 34727540
-
Telephone screening tests for functionally impaired hearing: current use in seven countries and development of a US version.J Am Acad Audiol. 2012 Nov-Dec;23(10):757-67. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.23.10.2. J Am Acad Audiol. 2012. PMID: 23169193 Clinical Trial.
-
[Hearing Loss and Speech Recognition in the Elderly].Laryngorhinootologie. 2017 Nov;96(11):759-764. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-119388. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Laryngorhinootologie. 2017. PMID: 29132188 Review. German.
-
Speech audiometry in noise-exposed workers: the SRT-PTA relationship revisited.Audiology. 1999 Jan-Feb;38(1):30-43. doi: 10.3109/00206099909073000. Audiology. 1999. PMID: 10052834 Review.
Cited by
-
The Accuracy of Self-Administered Web- and App-Based Tools for Audiometric Tests-A Systematic Review.Audiol Res. 2025 Jun 19;15(3):73. doi: 10.3390/audiolres15030073. Audiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40558412 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. 1 in 4 People Projected to have Hearing Problems by 2050. https://www.who.int/news/item/02-03-2021-who-1-in-4-people-projected-to-... (Accessed 13 June 2023).
-
- Loughrey, D. G., Kelly, M. E., Kelley, G. A., Brennan, S. & Lawlor, B. A. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg.144(2), 115–126. 10.1001/jamaoto.2017.2513 (2018).10.1001/jamaoto.2017.2513 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

