Preferences for attributes of oral antipsychotic treatments: results from a discrete-choice experiment in respondents with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder
- PMID: 39256654
- PMCID: PMC11389064
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-06034-1
Preferences for attributes of oral antipsychotic treatments: results from a discrete-choice experiment in respondents with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder
Abstract
Background: Antipsychotic medications are effective treatments for schizophrenia (SZ) and bipolar I disorder (BD-I), but when presented with different treatment options, there are tradeoffs that individuals make between clinical improvement and adverse effects. As new options become available, understanding the attributes of antipsychotic medications that are valued and the tradeoffs that individuals consider when choosing among them is important.
Methods: A discrete-choice experiment (DCE) was administered online to elicit preferences across 5 attributes of oral antipsychotics: treatment efficacy (i.e., improvement in symptom severity), weight gain over 6 months, sexual dysfunction, sedation, and akathisia. Eligible respondents were aged 18-64 years with a self-reported clinician diagnosis of SZ or BD-I.
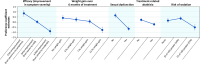
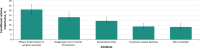
Results: In total, 144 respondents with SZ and 152 with BD-I completed the DCE. Of those with SZ, 50% identified themselves as female and 69.4% as White, with a mean (SD) age of 41.0 (10.1) years. Of those with BD-I, most identified themselves as female (69.7%) and as White (77.6%), with a mean (SD) age of 40.0 (10.7) years. In both cohorts, respondents preferred oral antipsychotics with better efficacy, less weight gain, no sexual dysfunction or akathisia, and lower risk of sedation. Treatment efficacy was the most important attribute, with a conditional relative importance (CRI) of 31.4% for respondents with SZ and 31.0% for those with BD-I. Weight gain (CRI = 21.3% and 23.1%, respectively) and sexual dysfunction (CRI = 23.4% and 19.2%, respectively) were adverse effects in this study that respondents most wanted to avoid. Respondents with SZ were willing to accept 9.8 lb of weight gain or > 25% risk of sedation for symptom improvement; those with BD-I were willing to accept 8.5 lb of weight gain or a > 25% risk of sedation.
Conclusions: In this DCE, treatment efficacy was the most important attribute of oral antipsychotic medications among respondents with SZ and BD-I. Weight gain and sexual dysfunction were the adverse effects respondents most wanted to avoid; however, both cohorts were willing to accept some weight gain or sedation to obtain better efficacy. These results highlight features that patients value in antipsychotic medications and how they balance benefits and risks when choosing among treatments.
Keywords: Discrete-choice experiment; Patient preference; Sedation; Treatment efficacy; Weight gain.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MJD and HRP are or were employees of Alkermes, Inc., at the time of the study and may own stock/options in the company. MB, CV, and CB are or were employees of RTI Health Solutions, a not-for-profit research institute that received funding from Alkermes, Inc., to conduct this study and collect the data used for this publication. LC consulted with Alkermes on this research and has served as a consultant for AbbVie/Allergan, Acadia, Adamas, Angelini, Astellas, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cadent Therapeutics, Cerevel, Clinilabs, COMPASS, Delpor, Eisai, Enteris BioPharma, HLS Therapeutics, Idorsia, INmune Bio, Impel, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Karuna, Lundbeck, Luye, Lyndra, MapLight, Marvin, MedAvante-ProPhase, Merck, Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma, Neumora, Neurocrine, Neurelis, Noema, Novartis, Noven, Otsuka, Ovid, Praxis, Recordati, Relmada, Reviva, Sage, Sumitomo/Sunovion, Supernus, Teva, University of Arizona, Vanda, and Wells Fargo, and one-off ad hoc consulting for individuals/entities conducting marketing, commercial, or scientific scoping research; and speaker for AbbVie/Allergan, Acadia, Alkermes, Angelini, Axsome, BioXcel, Eisai, Idorsia, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Lundbeck, Neurocrine, Noven, Otsuka, Recordati, Sage, Sunovion, Takeda, and Teva and CME activities organized by medical education companies such as Medscape, NACCME, NEI, Vindico, and universities and professional organizations/societies; owns stocks (small number of shares of common stock) in Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, J&J, Merck, and Pfizer purchased >10 years ago and has stock options for Reviva; and has received royalties/publishing income from Elsevier (topic editor,
Figures



References
-
- Doane MJ, Sajatovic M, Weiden PJ, O’Sullivan AK, Maher S, Bjorner JB, Sikora Kessler A, Carpenter-Conlin J, Bessonova L, Velligan DI. Antipsychotic treatment experiences of people with schizophrenia: patient perspectives from an online survey. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2020;14:2043–54. 10.2147/ppa.s270020 10.2147/ppa.s270020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bessonova L, Velligan DI, Weiden PJ, O’Sullivan AK, Yarlas A, Bayliss M, Baranwal N, Rychlec K, Carpenter-Conlin J, Doane MJ, et al. Antipsychotic treatment experiences of people with bipolar I disorder: patient perspectives from an online survey. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20:354. 10.1186/s12888-020-02767-x 10.1186/s12888-020-02767-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

