MicroRNAs in metabolism for precision treatment of lung cancer
- PMID: 39256662
- PMCID: PMC11384722
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-024-00632-3
MicroRNAs in metabolism for precision treatment of lung cancer
Abstract
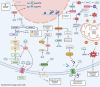
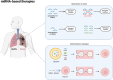
The dysregulation of miRNAs in lung cancer has been extensively documented, with specific miRNAs acting as both tumor suppressors and oncogenes, depending on their target genes. Recent research has unveiled the regulatory roles of miRNAs in key metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, fatty acid metabolism, and autophagy, which collectively contribute to the aberrant energy metabolism characteristic of cancer cells. Furthermore, miRNAs are increasingly recognized as critical modulators of the tumor microenvironment, impacting immune response and angiogenesis. This review embarks on a comprehensive journey into the world of miRNAs, unraveling their multifaceted roles, and more notably, their emerging significance in the context of cancer, with a particular focus on lung cancer. As we navigate this extensive terrain, we will explore the fascinating realm of miRNA-mediated metabolic rewiring, a phenomenon that plays a pivotal role in the progression of lung cancer and holds promise in the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Lung cancer; Metabolic reprogramming; Metabolism; miRNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wen W, Mai S-J, Lin H-X, Zhang M-Y, Huang J-L, Hua X, Lin C, Long Z-Q, Lu Z-J, Sun X-Q, et al. Identification of two microRNA signatures in whole blood as novel biomarkers for diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2019;17:186. 10.1186/s12967-019-1923-2. 10.1186/s12967-019-1923-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

