Tropical oils consumption and health: a scoping review to inform the development of guidelines in tropical regions
- PMID: 39256687
- PMCID: PMC11389204
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-19949-x
Tropical oils consumption and health: a scoping review to inform the development of guidelines in tropical regions
Abstract
Background: Tropical oils such as palm and coconut oils are renowned for their high saturated fat content and culinary versatility. However, their consumption has sparked debate regarding their health benefits and production concerns. The purpose of this review was to map existing evidence on the health benefits and challenges associated with the consumption of tropical oils.
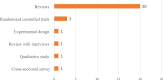
Method: The recommendations for conducting a scoping review by Arksey and O'Malley were followed. PubMed, Dimensions AI, Central, JSTOR Google, Google Scholar, and ProQuest databases were searched for relevant papers. The predetermined keywords used were Consumption" AND "Tropical oil," as well as "Health benefits" OR "Health challenges" AND "Tropical Countries." Peer-reviewed and grey literature published in English were eligible for this review.
Result: Tropical oils, such as palm and coconut oils, provide health benefits including essential vitamins (A and E) that enhance ocular health, boost immunity, and support growth. They are also recognised for their role in managing high blood sugar, obesity, and cholesterol levels, while offering antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These oils have wound-healing abilities and are commonly used in infant nutrition and traditional cooking. Nevertheless, prolonged and repeated use of tropical oils to high temperature can degrade vitamin E, whereas excessive intake may result in overdose. Health concerns include oxidative risks, diabetes, cancer, coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, and acrylamide formation due to production challenges excessive consumption. Additional issues include obesity, suboptimal oil production, misconceptions, regulatory obstacles, and preferences for alternative fats.
Conclusion: This review suggest that tropical oils provide essential health benefits, including vitamins and antioxidant properties, but pose significant health risks and production challenges, particularly when exposed to high temperatures and through excessive intake. Guidelines on the consumption of tropical oils in the tropical regions are necessary to regulate their consumption.
Keywords: Coconut oil; Consumption guidelines; Health benefits; Palm oil; Tropical oils.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest in this review.
Figures
References
-
- Meijaard E, Sheil D. The Moral minefield of ethical oil palm and sustainable development. Front Forests Global Change. 2019;2(455240). 10.3389/FFGC.2019.00022/BIBTEX.
-
- Naidu L, Moorthy R. A review of key sustainability issues in Malaysian palm oil industry. Sustain (Switzerland). 2021;13(19). 10.3390/su131910839.
-
- Absalome MA, Massara CC, Alexandre AA, Gervais K, Chantal GGA, Ferdinand D, Rhedoor AJ, Coulibaly I, George TG, Brigitte T, Marion M, Jean-Paul C. Biochemical properties, nutritional values, health benefits and sustainability of palm oil. Biochimie. 2020;178:81–95. 10.1016/J.BIOCHI.2020.09.019. 10.1016/J.BIOCHI.2020.09.019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ikegwu TM, Ezegbe CC, Odo EN, Okolo CA, Mba JC, Agu HO. Processing of Oilseeds in the Tropics: Prospects and Challenges. Oilseed Crops - Uses, Biology and Production.2023; 10.5772/intechopen.106247
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources