Validation of the parents' version of the KINDLR and Kiddy Parents questionnaire in a South African context
- PMID: 39256795
- PMCID: PMC11389106
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-024-02292-5
Validation of the parents' version of the KINDLR and Kiddy Parents questionnaire in a South African context
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess the usefulness of the parent version of the KINDLR and the additional items of the Kiddy Parents questionnaire in the South-African context and to validate it as an appropriate tool for measuring health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
Method: The ExAMIN Youth SA study was designed to investigate lifestyle behaviours, including psychosocial factors that may adversely impact on cardiovascular health of children. Construct validity was examined by using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, while internal consistency was tested by Cronbach's alpha. The final factor structure was confirmed by model fit indices.
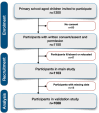
Results: The study included children (n = 1088) aged between 5 and 10 years in North-West, South Africa. The reliability coefficients of the original factors could not be reproduced in this data set, with the Cronbach's alphas ranging between 0.46 and 0.78. With exploratory factor analysis, including the additional items, our data supported a 7-factor structure with acceptable internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha: 0.68-0.79; Omega: 0.75-0.85) and acceptable model fit indices (CFI: 0.91; TLI: 0.90; RMSEA: 0.05; SRMR: 0.07). Two factors (emotional wellbeing and everyday functioning) further split into separate factors for positive and negative experiences related to each of these dimensions.
Conclusion: We confirmed a new factor structure of the parent version of the KINDLR and the additional items of the Kiddy Parents questionnaire, which can be used in the African context. Although the new factor structure has great overlap with the original structure, some items did not contribute to the factors as expected. Language and cultural differences between the original German group and the current South African study group resulted in a different factor structure.
Keywords: Children; Health related quality of life; KINDLR; South Africa; Validation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Parent-reported Health-Related Quality of Life in Spanish pre-schoolers: Psychometric properties of the Kiddy-KINDL-R].An Pediatr (Engl Ed). 2019 May;90(5):263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2018.04.019. Epub 2018 Jul 6. An Pediatr (Engl Ed). 2019. PMID: 31056090 Spanish.
-
Self-reported health-related quality of life in kindergarten children: psychometric properties of the Kiddy-KINDL.Public Health. 2015 Jul;129(7):889-95. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2015.04.020. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26051961
-
Psychometric evaluation and wording effects on the Chinese version of the parent-proxy Kid-KINDL.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2016 Sep 5;14(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12955-016-0526-3. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2016. PMID: 27595602 Free PMC article.
-
Transcultural adaptation to Spain of the CDPQOL questionnaire specific for coeliac children.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Aug;183(8):3233-3241. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05589-1. Epub 2024 May 3. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38700691
-
Assessing health-related quality of life in young Japanese children with chronic conditions: Preliminary validation of the DISABKIDS smiley measure.BMC Pediatr. 2017 Apr 5;17(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0854-4. BMC Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28381217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buehler C. Family processes and children’s and adolescents’ well-being. J Marriage Family. 2020;82(1):145–74.10.1111/jomf.12637 - DOI
-
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. In: Hillsdale NJ, editor. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc., Hillsdale, NJ., ed. -: Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc.; 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous