Sex differences in neural networks recruited by frontloaded binge alcohol drinking
- PMID: 39256902
- PMCID: PMC11387202
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13434
Sex differences in neural networks recruited by frontloaded binge alcohol drinking
Abstract
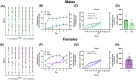
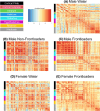
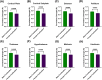
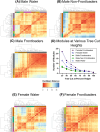
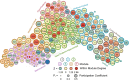
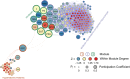
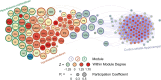
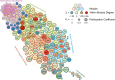
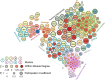
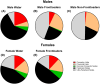
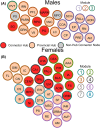
Frontloading is an alcohol drinking pattern where intake is skewed towards the onset of access. This study aimed to identify brain regions involved in frontloading. Whole brain imaging was performed in 63 C57Bl/6J (32 female, 31 male) mice that underwent 8 days of binge drinking using drinking-in-the-dark (DID). On Days 1-7 mice received 20% (v/v) alcohol or water for 2 h. Intake was measured in 1-min bins using volumetric sippers. On Day 8 mice were perfused 80 min into the DID session and brains were extracted. Brains were processed to stain for Fos protein using iDISCO+. Following light sheet imaging, ClearMap2.1 was used to register brains to the Allen Brain Atlas and detect Fos+ cells. For network analyses, Day 8 drinking patterns were used to characterize mice as frontloaders or non-frontloaders using a change-point analysis. Functional correlation matrices were calculated for each group from log10 Fos values. Euclidean distances were calculated from these R values and clustering was used to determine modules (highly connected groups of brain regions). In males, alcohol access decreased modularity (three modules in both frontloaders and non-frontloaders) as compared to water (seven modules). In females, an opposite effect was observed. Alcohol access (nine modules for frontloaders) increased modularity as compared to water (five modules). Further, different brain regions served as hubs in frontloaders as compared to control groups. In conclusion, alcohol consumption led to fewer, but more densely connected, groups of brain regions in males but not females and we identify several brain-wide signatures of frontloading.
Keywords: binge drinking; frontloading; iDISCO+.
© 2024 The Author(s). Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Update of
-
Sex Differences in Neural Networks Recruited by Frontloaded Binge Alcohol Drinking.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 9:2024.02.08.579387. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.08.579387. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Addict Biol. 2024 Sep;29(9):e13434. doi: 10.1111/adb.13434. PMID: 38370732 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AA029985/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AA007611/Indiana Alcohol Research Center
- R01 AA029985/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA007462/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA023786/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AA027301/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA027301/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA007611/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007462/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA023786/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA029409/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AA027301/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA007611/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

