Same-Day Repeatability and 28-Day Reproducibility of Xenon MRI Ventilation in Children With Cystic Fibrosis in a Multi-Site Trial
- PMID: 39257323
- PMCID: PMC11896927
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.29605
Same-Day Repeatability and 28-Day Reproducibility of Xenon MRI Ventilation in Children With Cystic Fibrosis in a Multi-Site Trial
Abstract
Background: MRI with xenon-129 gas (Xe MRI) can assess airflow obstruction and heterogeneity in lung diseases. Specifically, Xe MRI may represent a sensitive modality for future therapeutic trials of cystic fibrosis (CF) therapies. The reproducibility of Xe MRI has not yet been assessed in the context of a multi-site study.
Purpose: To determine the same-day repeatability and 28-day reproducibility of Xe MRI in children with CF.
Study type: Four-center prospective, longitudinal.
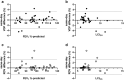
Population: Thirty-eight children (18 females, 47%), median interquartile range (IQR) age 12 (9-14) years old, with mild CF (forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) ≥85% predicted).
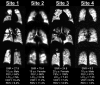
Field strength/sequence: 3-T, two-dimensional (2D) gradient-echo (GRE) sequence.
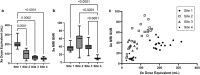
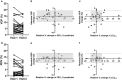
Assessment: Xe MRI, FEV1, and nitrogen multiple-breath wash-out for lung-clearance index (LCI2.5) were performed. To assess same-day reproducibility, Xe MRI was performed twice within the first visit, and procedures were repeated at 28 days. Xe hypoventilation was quantified using ventilation-defect percentage (VDP) and reader-defect volume (RDV). For VDP, hypoventilated voxels from segmented images were identified using a threshold of <60% mean whole-lung signal and expressed as a percentage of the lung volume. For RDV, hypoventilation was identified by two trained readers and expressed as a percentage.
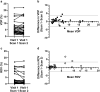
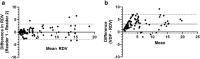
Statistical tests: Inter-site comparisons were conducted using Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric tests with Dunn's multiple-comparisons tests. Differences for individuals were assessed using Wilcoxon matched-pairs tests. Bland-Altman tests were used to evaluate same-day repeatability, 28-day reproducibility, and inter-reader agreement. A P-value ≤0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Median FEV1 %-predicted was 96.8% (86%-106%), and median LCI2.5 was 6.6 (6.3-7.4). Xe MRI had high same-day reproducibility (mean VDP difference 0.12%, 95% limits of agreement [-3.2, 3.4]; mean RDV difference 0.42% [-2.5, 3.3]). At 28 days, 26/31 participants (84%) fell within the same-day 95% limits of agreement.
Data conclusion: Xe MRI may offer excellent same-day and short-term reproducibility.
Evidence level: 2 TECHNICAL EFFICACY: Stage 2.
Keywords: Xe MRI; cystic fibrosis; pediatrics; ventilation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Mall MA, Burgel P‐R, Castellani C, Davies JC, Salathe M, Taylor‐Cousar JL. Cystic fibrosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2024;10(1):53. - PubMed
-
- David M, Benlala I, Bui S, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of bronchial changes in cystic fibrosis patients undergoing elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor therapy using lung MRI with ultrashort echo‐times. J Magn Reson Imaging 2024;60(1):116‐124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

