This is a preprint.
Increased burden of rare risk variants across gene expression networks predisposes to sporadic Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39257816
- PMCID: PMC11384021
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.08.30.610195
Increased burden of rare risk variants across gene expression networks predisposes to sporadic Parkinson's disease
Update in
-
Increased burden of rare risk variants across gene expression networks predisposes to sporadic Parkinson's disease.Cell Rep. 2025 May 27;44(5):115636. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115636. Epub 2025 May 1. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40317721 Free PMC article.
Abstract
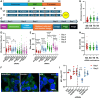
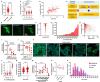
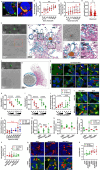
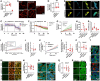
Alpha-synuclein (αSyn) is an intrinsically disordered protein that accumulates in the brains of patients with Parkinson's disease and forms intraneuronal inclusions called Lewy Bodies. While the mechanism underlying the dysregulation of αSyn in Parkinson's disease is unclear, it is thought that prionoid cell-to-cell propagation of αSyn has an important role. Through a high throughput screen, we recently identified 38 genes whose knock down modulates αSyn propagation. Follow up experiments were undertaken for two of those genes, TAX1BP1 and ADAMTS19, to study the mechanism with which they regulate αSyn homeostasis. We used a recently developed M17D neuroblastoma cell line expressing triple mutant (E35K+E46K+E61K) "3K" αSyn under doxycycline induction. 3K αSyn spontaneously forms inclusions that show ultrastructural similarities to Lewy Bodies. Experiments using that cell line showed that TAX1BP1 and ADAMTS19 regulate how αSyn interacts with lipids and phase separates into inclusions, respectively, adding to the growing body of evidence implicating those processes in Parkinson's disease. Through RNA sequencing, we identified several genes that are differentially expressed after knock-down of TAX1BP1 or ADAMTS19. Burden analysis revealed that those differentially expressed genes (DEGs) carry an increased frequency of rare risk variants in Parkinson's disease patients versus healthy controls, an effect that was independently replicated across two separate cohorts (GP2 and AMP-PD). Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) showed that the DEGs cluster within modules in regions of the brain that develop high degrees of αSyn pathology (basal ganglia, cortex). We propose a novel model for the genetic architecture of sporadic Parkinson's disease: increased burden of risk variants across genetic networks dysregulates pathways underlying αSyn homeostasis, thereby leading to pathology and neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest M.M.M. is an inventor of filed and issued patents related to α-synuclein. M.M.M. is a founder of MentiNova, Inc. E.K. is a member of the EMBO Scientific Exchange Grants Advisory Board.
Figures



References
-
- S A. (2010) Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO–the Open Visualization Tool. Modelling Simul Mater Sci Eng 18
-
- Banfi S, Servadio A, Chung MY, Kwiatkowski TJ Jr., McCall AE, Duvick LA, Shen Y, Roth EJ, Orr HT, Zoghbi HY (1994) Identification and characterization of the gene causing type 1 spinocerebellar ataxia. Nat Genet 7: 513–520 - PubMed
-
- Bauerlein FJB, Saha I, Mishra A, Kalemanov M, Martinez-Sanchez A, Klein R, Dudanova I, Hipp MS, Hartl FU, Baumeister W, Fernandez-Busnadiego R (2017) In Situ Architecture and Cellular Interactions of PolyQ Inclusions. Cell 171: 179–187 e110 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
