Artificial intelligence and wheezing in children: where are we now?
- PMID: 39257890
- PMCID: PMC11385867
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1460050
Artificial intelligence and wheezing in children: where are we now?
Abstract
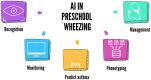
Wheezing is a common condition in childhood, and its prevalence has increased in the last decade. Up to one-third of preschoolers develop recurrent wheezing, significantly impacting their quality of life and healthcare resources. Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies have recently been applied in paediatric allergology and pulmonology, contributing to disease recognition, risk stratification, and decision support. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has shaped healthcare systems, resulting in an increased workload and the necessity to reduce access to hospital facilities. In this view, AI and Machine Learning (ML) approaches can help address current issues in managing preschool wheezing, from its recognition with AI-augmented stethoscopes and monitoring with smartphone applications, aiming to improve parent-led/self-management and reducing economic and social costs. Moreover, in the last decade, ML algorithms have been applied in wheezing phenotyping, also contributing to identifying specific genes, and have been proven to even predict asthma in preschoolers. This minireview aims to update our knowledge on recent advancements of AI applications in childhood wheezing, summarizing and discussing the current evidence in recognition, diagnosis, phenotyping, and asthma prediction, with an overview of home monitoring and tele-management.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; asthma; digital health; machine learning; wheezing.
Copyright © 2024 Venditto, Morano, Piazza, Zaffanello, Tenero, Piacentini and Ferrante.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor AL declared past co-authorships with the authors MP, GP, and GF.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources