Serum Level Alteration of IL-6, IL-1 β, and IFN- γ in Groups of Healthy Adults with Oxidative DNA Damage in Najaf Governorate
- PMID: 39257966
- PMCID: PMC11383644
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/9048536
Serum Level Alteration of IL-6, IL-1 β, and IFN- γ in Groups of Healthy Adults with Oxidative DNA Damage in Najaf Governorate
Abstract
Background: Najaf governorate was recorded as one of the most polluted Iraqi governorates with increased cancer, autoimmune, and abortion cases. Study Groups. A total of 88 adult volunteers from three test groups were divided based on their inhabitance in different geographical regions in Najaf governorate. Group 1 (G1; n, 29) inhabitants of Al-Ansar, Al-Abbaseyeh, and Al-Manathera districts, Group 2 (G2; n, 27) inhabitants of 22 different scattered districts of the governorate, Group 3 (G3; n, 32) inhabitants of Kufa city and center districts in the old Najaf city. According to previous authors' findings, all participants had uranium contamination in their urine and blood samples, and also, they had DNA damage according to the level of urinary 8-OHdG compound. The control group 4 (G4; n, 25) were adult healthy Iraqi volunteers who were residents of the Sulaimaniyah governorate, which has low-level uranium pollution. The present study aims to determine the effect of uranium pollution and DNA damage on the immune system function in terms of estimating the levels of serum interleukin (IL)-6, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and IL-1 beta (β).
Method: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Sandwich method technique) was used for estimating the serum cytokines levels in test and control groups.
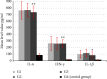
Results: A significant elevation of cytokines levels was reported as compared with the control groups (p ≤ 0.01). The level of IL-6 was 764.64 ± 24.12 pg/ml, 768.87 ± 19.64 pg/ml, and 735.62 ± 18.47 in G1, G2, and G3, respectively. The level of IFN-γ was 264.55 ± 19.17 pg/ml, 259 ± 18.76 pg/ml, and 261.20 ± 12.99 pg/ml for G1, G2, and G3, respectively. The level of IL-1β was 99.85 ± 10.81 pg/ml, 116.8 ± 10.71 pg/ml, and 83 ± 19.24 pg/ml in G1, G2, and G3, respectively. The levels of IL-6, IFN-γ, and IL-1β were 86.5 ± 22.9 pg/ml, 19.4 ± 2.8 pg/ml, and 16.1 ± 3.2 pg/ml in the sera of control (G4). The results showed significant statistical elevation with the corresponding p value cut-off p ≤ 0.01 in IL-6, IFN-γ, and IL-1β in the sera of three test groups as compared with the results of the control group.
Conclusion: The change in the proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IFN-γ, and IL-1β) levels indicates a persistent inflammatory response in the participants and may reflect immune system impairment as a consequence of exposure to long-term low-dose ionizing radiation.
Copyright © 2024 Dhuha S. Saleh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Özkara A., Akyıl D., Konuk M. In Environmental Health Risk-Hazardous Factors to Living Species . Norderstedt, Germany: Books on Demand; 2016. Pesticides, environmental pollution, and health.
-
- Wright J. EnvironmentalChemistry . 2nd. London, UK: Routledge Publishing; 2005.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

