Peptic ulcer induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors successfully treated with glucocorticoids: A report of three cases and a literature review
- PMID: 39258241
- PMCID: PMC11384188
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12699
Peptic ulcer induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors successfully treated with glucocorticoids: A report of three cases and a literature review
Abstract
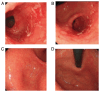
In recent decades, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have emerged as safer and less disruptive alternatives to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy for certain patients with tumours. ICIs serve a synergistic role alongside conventional therapies by manipulating the immune system to recognise and target tumour cells. However, excessive activation of the immune system can lead to immune-related adverse events including pneumonia, myocarditis and colitis, which pose serious and even fatal risks. In the present case series, three patients with a thoracic tumour with an ICI-induced peptic ulcer triggered by programmed cell death protein 1 antibodies (diagnosed by gastrointestinal endoscopy) are presented. These cases were successfully treated with corticosteroids. The diagnostic and treatment processes undertaken for these patients underscore the requirement to comprehensively understand the mechanism of ICI-induced peptic ulcer. Moreover, the relevant literature was also reviewed in the present study.
Keywords: ICI-induced peptic ulcer; adverse effects; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immunotherapy; thoracic tumours.
Copyright: © 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
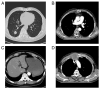
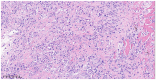
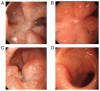
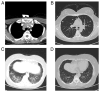
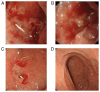
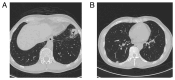
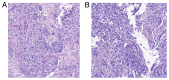
References
-
- Coutzac C, Adam J, Soularue E, Collins M, Racine A, Mussini C, Boselli L, Kamsukom N, Mateus C, Charrier M. Colon immune-related adverse events: Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 blockade induce distinct immunopathological entities. J Crohns Colitis. 2017;11:1238–1246. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx081. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
