Effect of Smoking on Seminal Plasma Vitamin B6 in Fertile and Subfertile Men
- PMID: 39258263
- PMCID: PMC11387083
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/8159993
Effect of Smoking on Seminal Plasma Vitamin B6 in Fertile and Subfertile Men
Abstract
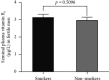
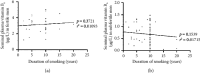
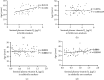
Despite extensive documentation of the negative consequences of smoking on a wide range of diseases and disorders, the direct effect of smoking on seminal plasma vitamin B6 (vitB6) concentration is not addressed yet. Here, we attempted to examine the influence of smoking on the levels of seminal plasma vitB6 in fertile and subfertile males. One hundred and ninety-five participants were categorized into two groups: fertile men (smokers (n = 32), nonsmokers (n = 43)) and subfertile men (smokers (n = 65), nonsmokers (n = 55)). According to the World Health Organization criteria, conventional semen analysis was performed for all subjects involved in the study. The concentration of vitB6 in semen samples was measured by high-performance liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry. There was no significant difference in the mean seminal plasma concentrations of vitB6 in smokers versus nonsmokers in both fertile (p=0.5096) and subfertile (p=0.5224) groups. Besides, no significant correlations were observed between seminal plasma concentration of vitB6, duration of smoking, and men's age in all tested groups. In conclusion, these findings elucidate that smoking has no significant impact on the levels of seminal plasma vitB6 in both fertile and subfertile men.
Copyright © 2024 Shefa' Muneer Aljabali and Saleem Ali Banihani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Elbarbary N. S., Ismail E. A. R., Zaki M. A., Darwish Y. W., Ibrahim M. Z., El-Hamamsy M. J. C. N. Vitamin B complex supplementation as a homocysteine-lowering therapy for early stage diabetic nephropathy in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition . 2020;39(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.01.006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

