Pulsed Field Ablation to Treat Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Safety and Effectiveness in the AdmIRE Pivotal Trial
- PMID: 39258362
- PMCID: PMC11458102
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.070333
Pulsed Field Ablation to Treat Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Safety and Effectiveness in the AdmIRE Pivotal Trial
Abstract
Background: Evidence from clinical trials of early pulsed field ablation (PFA) systems in treating atrial fibrillation has demonstrated their promising potential to reduce complications associated with conventional thermal modalities while maintaining efficacy. However, the lack of a fully integrated mapping system, a staple technology of most modern electrophysiology procedures, poses limitations in lesion creation and workflow options. A novel variable-loop PFA catheter integrated with an electroanatomic mapping system has been developed that allows for real-time nonfluoroscopic procedural guidance and lesion indexing as well as feedback of tissue-to-catheter proximity. AdmIRE (Assessment of Safety and Effectiveness in Treatment Management of Atrial Fibrillation With the Bosense-Webster Irreversible Electroporation Ablation System), a multicenter, single-arm, Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption study, evaluated the long-term safety and effectiveness of this integrated PFA system in a large United States-based drug-refractory symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation patient population.
Methods: Using the PFA catheter with a compatible electroanatomic mapping system, patients with drug-refractory symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation underwent pulmonary vein isolation. The primary safety end point was primary adverse event within 7 days of ablation. The primary effectiveness end point was a composite end point that included 12-month freedom from documented atrial tachyarrhythmia (ie, atrial fibrillation, atrial tachycardia, atrial flutter) episodes, failure to achieve pulmonary vein isolation, use of a nonstudy catheter for pulmonary vein isolation, repeat procedure (except for one redo during blanking), taking a new or previously failed class I or III antiarrhythmic drug at higher dose after blanking, or direct current cardioversion after blanking.
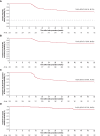
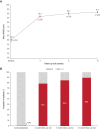
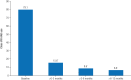
Results: At 30 centers, 277 patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (61.5±10.3 years of age; 64.3% male) in the pivotal cohort underwent PFA. More than 25% of the procedures were performed without fluoroscopy. Median (Q1, Q3) pulmonary vein isolation procedure, fluoroscopy, and transpired PFA application times were 81.0 (61.0, 112.0), 7.1 (0.00, 14.3), and 31.0 (24.8, 40.9) minutes, respectively. The primary adverse event rate was 2.9% (8 of 272), with the most common complication being pericardial tamponade. The 12-month primary effectiveness end point was 74.6%. The 1-year freedom from atrial fibrillation, atrial tachycardia, or atrial flutter recurrence rate after blanking was 75.4%. Substantial improvements in quality of life were observed as early as 3 months after the procedure, concurrent with a reduction in multiple health care use measures.
Conclusions: AdmIRE confirmed the safety and effectiveness of the variable-loop PFA catheter, with short procedure and PFA application times and low fluoroscopy exposure.
Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT05293639.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; catheters; pulmonary veins.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Reddy reports receiving consulting fees and grant support from Biosense-Webster; unrelated to this article, serves as a consultant for and has equity in Ablacon, Acutus Medical, Affera-Medtronic, Anumana, Apama Medical-Boston Scientific, APN Health, Aquaheart, Atacor, Autonomix, Axon Therapies, Backbeat, BioSig, CardiaCare, Cardiofocus, CardioNXT/AFTx, Circa Scientific, CoRISMA, Corvia Medical, Dinova-Hangzhou DiNovA EP Technology, East End Medical, EPD-Philips, EP Frontiers, Epix Therapeutics-Medtronic, EpiEP, Eximo, Farapulse-Boston Scientific, Field Medical, Focused Therapeutics, HRT, Intershunt, Javelin, Kardium, Keystone Heart, Laminar Medical, LuxMed, Medlumics, Middlepeak, Neutrace, Nuvera-Biosense Webster, Oracle Health, Restore Medical, Sirona Medical, SoundCath, and Valcare; unrelated to this work, has served as a consultant for Abbott, Adagio Medical, Append Medical, AtriAN, BioTel Heart, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Cairdac, Cardionomic, CoreMap, Fire1, Gore & Associates, Impulse Dynamics, Medtronic, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Philips, and Pulse Biosciences; and unrelated to this work, has equity in Atraverse, DRS Vascular, Manual Surgical Sciences, Newpace, Nyra Medical, Soundcath, Surecor, and Vizaramed. Dr Calkins receives consulting fees from Biosense Webster and Boston Scientific and payment for honoraria from Boston Scientific and Medtronic. Dr Mansour reports grants from Biosense Webster, Inc, and Boston Scientific; consulting fees from Biosense Webster, Inc, Boston Scientific, Philips, and Medtronic; support for attending meetings/travel from Biosense Webster, Inc, and Boston Scientific; and stock/stock options from NewPace Limited and EPD Solutions. Dr Wazni serves as a consultant for Biosense Webster. Dr Di Biase is a consultant for Biosense Webster, Stereoataxis, and Rhythm Management, and has received speaker honoraria/travel from Biosense Webster, St. Jude Medical (now Abbott), Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Biotronik, Atricure, Baylis, and Zoll. Drs Bahu and Liu have nothing to disclose. Dr Newton serves as a consultant for Biosense Webster. Dr Sauer receives grants from Biosense Webster and Medtronic and consulting fees from Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, and Abbott. Dr Goyal receives consulting fees from Biosense Webster and Medtronic. Dr Iyer receives consulting fees from Biosense Webster. Dr Nair serves as a consultant for and receives research grants from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Biosense Webster, and Adagio, and receives research grants from Laminar. Dr Athill receives consulting fees from Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Biosense Webster, and payment/honoraria from Zoll and Janssen. Dr Hussein receives research grants from Boston Scientific and serves on steering committees for Biosense Webster. Dr Whalen serves on the advisory board for Biosense Webster. Dr Melby serves as a consultant for and receives research grants from Biosense Webster. Dr Natale serves as a consultant for Abbott, Biosense Webster, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and iRhythm.
Figures

References
-
- Reddy VY, Anic A, Koruth J, Petru J, Funasako M, Minami K, Breskovic T, Sikiric I, Dukkipati SR, Kawamura I, et al. Pulsed field ablation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:1068–1080. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.07.007 - PubMed
-
- Reddy VY, Anter E, Rackauskas G, Peichl P, Koruth JS, Petru J, Funasako M, Minami K, Natale A, Jais P, et al. Lattice-tip focal ablation catheter that toggles between radiofrequency and pulsed field energy to treat atrial fibrillation: a first-in-human trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2020;13:e008718. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.120.008718 - PubMed
-
- Reddy VY, Dukkipati SR, Neuzil P, Anic A, Petru J, Funasako M, Cochet H, Minami K, Breskovic T, Sikiric I, et al. Pulsed field ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: 1-year outcomes of IMPULSE, PEFCAT, and PEFCAT II. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2021;7:614–627. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2021.02.014 - PubMed
-
- Reddy VY, Neuzil P, Koruth JS, Petru J, Funosako M, Cochet H, Sediva L, Chovanec M, Dukkipati SR, Jais P. Pulsed field ablation for pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.04.021 - PubMed
-
- Schmidt B, Bordignon S, Neven K, Reichlin T, Blaauw Y, Hansen J, Adelino R, Ouss A, Futing A, Roten L, et al. European Real-World Outcomes With Pulsed Field Ablation in Patients With Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation: lessons from the multi-centre EU-PORIA registry. Europace. 2023;25:euad185. doi: 10.1093/europace/euad185 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

