Recent updates on the influence of iron and magnesium on vascular, renal, and adipose inflammation and possible consequences for hypertension
- PMID: 39258532
- PMCID: PMC11451934
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003829
Recent updates on the influence of iron and magnesium on vascular, renal, and adipose inflammation and possible consequences for hypertension
Abstract
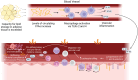
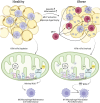
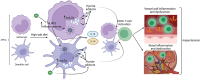
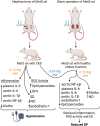
The inflammatory status of the kidneys, vasculature, and perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) has a significant influence on blood pressure and hypertension. Numerous micronutrients play an influential role in hypertension-driving inflammatory processes, and recent reports have provided bases for potential targeted modulation of these micronutrients to reduce hypertension. Iron overload in adipose tissue macrophages and adipocytes engenders an inflammatory environment and may contribute to impaired anticontractile signalling, and thus a treatment such as chelation therapy may hold a key to reducing blood pressure. Similarly, magnesium intake has proven to greatly influence inflammatory signalling and concurrent hypertension in both healthy animals and in a model for chronic kidney disease, demonstrating its potential clinical utility. These findings highlight the importance of further research to determine the efficacy of micronutrient-targeted treatments for the amelioration of hypertension and their potential translation into clinical application.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- The World Health Organisation 2023. Hypertension. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension [Accessed 10 November 2023].
-
- Arima H, Barzi F, Chalmers J. Mortality patterns in hypertension. J Hypertens 2011; 29: (Suppl 1): S3–S7. - PubMed
-
- Elliot WJ. Systemic hypertension. Curr Probl Cardiol 2007; 32:201–259. - PubMed
-
- Oparil S, Zaman MA, Calhoun DA. Pathogenesis of hypertension. Ann Intern Med 2003; 139:761–776. - PubMed
-
- Bataillard A, Freiche JC, Vincent M, Sassard J, Touraine JL. Antihypertensive effect of neonatal thymectomy in the genetically hypertensive LH rat. Thymus 1986; 8:321–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

