Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization to Elucidate the Relationship Between Healthy Sleep, Brains, and Hearts
- PMID: 39258560
- PMCID: PMC11935631
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.037394
Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization to Elucidate the Relationship Between Healthy Sleep, Brains, and Hearts
Keywords: Editorials; Mendelian randomization analysis; brain; heart; sleep.
Figures
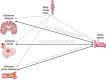
Comment on
-
Causal Associations of Sleep Apnea With Alzheimer Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Sep 17;13(18):e033850. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.033850. Epub 2024 Sep 11. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39258525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lutsey PL, Misialek JR, Mosley TH, Gottesman RF, Punjabi NM, Shahar E, MacLehose R, Ogilvie RP, Knopman D, Alonso A. Sleep characteristics and risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14:157–166. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.06.2269 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

