Establishing national hospital costing systems: insights from the qualitative assessment of cost surveillance pilot in Indian hospitals
- PMID: 39260852
- PMCID: PMC11409349
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-082965
Establishing national hospital costing systems: insights from the qualitative assessment of cost surveillance pilot in Indian hospitals
Abstract
Objective: The Indian Government launched Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY), the world's largest health insurance scheme, in 2018. To reform pricing and gather evidence on healthcare costs, a hospital cost-surveillance pilot was initiated among PM-JAY empanelled hospitals. We analysed the process and challenges from both healthcare providers and payer agency's perspectives and offer recommendations for implementing similar systems in lower- and middle-income countries.
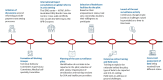
Design: We employed an open-ended, descriptive and qualitative study design using in-depth interviews (IDI) as the data collection strategy.
Settings: The interviews were conducted in both virtual and face-to-face modes depending on the convenience of the participants. The IDIs for the National Health Authority (NHA) officials and all providers in Kerala were conducted virtually, while face-to-face interviews were conducted and in Haryana and Chhattisgarh.
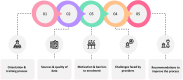
Participants: Staff from 21 hospitals in three states (Haryana, Chhattisgarh and Kerala), including officials from State Health Agency (n=5) and NHA (n=3) were interviewed.
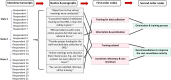
Results: The findings highlight significant challenges in reporting cost data at the hospital level. These include a shortage of trained staff, leading to difficulties in collecting comprehensive and high-quality data. Additionally, the data collection process is resource-intensive and time-consuming, putting strain on limited capacity. Operational issues with transaction management system, such as speed, user-friendliness and frequent page expirations, also pose obstacles. Finally, current patient records data has gaps, in terms of quantity and quality, to be directly put to use for pricing.
Conclusion: Accurate cost data is vital for health policy decisions. Capacity building across healthcare levels is needed for precise cost collection. Integration into digital infrastructure is key to avoid burdening providers and ensure quality data capture.
Keywords: Health Workforce; Health policy; PUBLIC HEALTH.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SP has formerly served as the Executive Director of the National Health Authority and BG is currently serving as the Additional Chief Executive Officer of the National Health Authority, Government of India.
Figures

References
-
- Sharma A, Prinja S. Universal health coverage: current status and future roadmap for India. Int J Non-Commun Dis. 2018;3:78. doi: 10.4103/jncd.jncd_24_18. - DOI
-
- National Health Authority. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Government of India About pradhan mantri jan arogya yojana (pm-jay) 2022. [21-May-2022]. https://pmjay.gov.in/about/pmjay Available. Accessed.
-
- World Health Organization . Case-based payment systems for hospital funding in Asia an investigation of current status and future directions. OECD Publishing; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
