Neurophysiology of Effortful Listening: Decoupling Motivational Modulation from Task Demands
- PMID: 39261007
- PMCID: PMC11529814
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0589-24.2024
Neurophysiology of Effortful Listening: Decoupling Motivational Modulation from Task Demands
Abstract
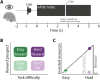
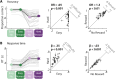
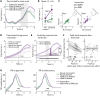
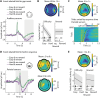
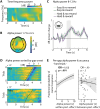
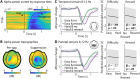
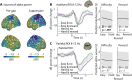
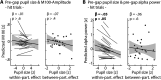
In demanding listening situations, a listener's motivational state may affect their cognitive investment. Here, we aim to delineate how domain-specific sensory processing, domain-general neural alpha power, and pupil size as a proxy for cognitive investment encode influences of motivational state under demanding listening. Participants (male and female) performed an auditory gap-detection task while the pupil size and the magnetoencephalogram were simultaneously recorded. Task demand and a listener's motivational state were orthogonally manipulated through changes in gap duration and monetary-reward prospect, respectively. Whereas task difficulty impaired performance, reward prospect enhanced it. The pupil size reliably indicated the modulatory impact of an individual's motivational state. At the neural level, the motivational state did not affect auditory sensory processing directly but impacted attentional postprocessing of an auditory event as reflected in the late evoked-response field and alpha-power change. Both pregap pupil dilation and higher parietal alpha power predicted better performance at the single-trial level. The current data support a framework wherein the motivational state acts as an attentional top-down neural means of postprocessing the auditory input in challenging listening situations.
Keywords: cognitive demand; event-related field; gap detection; motivation intensity theory; neural alpha power; pupil dilation; reward prospect.
Copyright © 2024 the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
