Multiscale mapping of transcriptomic signatures for cardiotoxic drugs
- PMID: 39261481
- PMCID: PMC11390749
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52145-4
Multiscale mapping of transcriptomic signatures for cardiotoxic drugs
Abstract
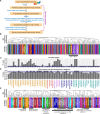
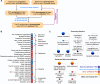
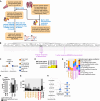
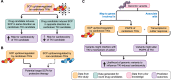
Drug-induced gene expression profiles can identify potential mechanisms of toxicity. We focus on obtaining signatures for cardiotoxicity of FDA-approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in human induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes, using bulk transcriptomic profiles. We use singular value decomposition to identify drug-selective patterns across cell lines obtained from multiple healthy human subjects. Cellular pathways affected by cardiotoxic TKIs include energy metabolism, contractile, and extracellular matrix dynamics. Projecting these pathways to published single cell expression profiles indicates that TKI responses can be evoked in both cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts. Integration of transcriptomic outlier analysis with whole genomic sequencing of our six cell lines enables us to correctly reidentify a genomic variant causally linked to anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity and predict genomic variants potentially associated with TKI-induced cardiotoxicity. We conclude that mRNA expression profiles when integrated with publicly available genomic, pathway, and single cell transcriptomic datasets, provide multiscale signatures for cardiotoxicity that could be used for drug development and patient stratification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Dorato, M. A. & Buckley, L. A. Toxicology in the drug discovery and development process. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol.Chapter 10, Unit10 13 10.1002/0471141755.ph1003s32 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG008098/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U54HG008098/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 75F40119C10021/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U.S. Food & Drug Administration)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

