A prospective 10-year follow-up study after sublobar resection for ground-glass opacity-dominant lung cancer
- PMID: 39261621
- PMCID: PMC11390874
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-72248-8
A prospective 10-year follow-up study after sublobar resection for ground-glass opacity-dominant lung cancer
Abstract
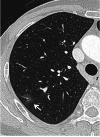
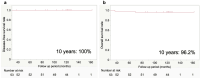
This single-arm multi-institutional prospective study aimed to evaluate the 10-year outcomes of sublobar resection for small-sized ground-glass opacity-dominant lung cancer. Among 73 patients prospectively enrolled from 13 institutions between November 2006 and April 2012, 53 ground-glass opacity-dominant lung cancer patients underwent sublobar resection with wedge resection as the first choice. The inclusion criteria were maximum tumor size of 8-20 mm; ≥ 80% ground-glass opacity ratio on high-resolution computed tomography; lower 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation than the mediastinum; intraoperative pathological diagnosis of adenocarcinoma in situ; and no cancer cells on intraoperative cut margins. The primary endpoint was a 10-year disease-specific survival. The 53 eligible patients had a mean tumor size of 14 ± 3.4 mm and a mean ground-glass opacity ratio of 95.9 ± 7.2%. Wedge resection and segmentectomy were performed in 39 and 14 patients, respectively. The final pathological diagnoses were adenocarcinoma in situ in 47 patients (88.7%) and adenocarcinoma with mixed subtype in 6 patients (11.3%). The 10-year disease-specific survival and overall survival were 100% and 96.2%, respectively, during a median follow-up period of 120 months (range, 37-162 months). Ground-glass opacity-dominant small lung cancer is cured by sublobar resection when patients are strictly selected by the inclusion criteria of this study.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Ground-glass opacity; Lung cancer; Positron emission tomography; Sublobar resection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A prospective 5-year follow-up study after limited resection for lung cancer with ground-glass opacity.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018 Apr 1;53(4):849-856. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezx418. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018. PMID: 29236995 Clinical Trial.
-
A single-arm study of sublobar resection for ground-glass opacity dominant peripheral lung cancer.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Jan;163(1):289-301.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.09.146. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 33487427
-
Appropriate sublobar resection choice for ground glass opacity-dominant clinical stage IA lung adenocarcinoma: wedge resection or segmentectomy.Chest. 2014 Jan;145(1):66-71. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-1094. Chest. 2014. PMID: 24551879
-
Surgical treatments for multiple primary adenocarcinoma of the lung.Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Oct;78(4):1194-9. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.03.102. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15464469 Review.
-
Prognostic value of CT-defined ground-glass opacity in early-stage lung adenocarcinomas: a single-center study and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2024 Mar;34(3):1905-1920. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10160-x. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37650971
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous