Promotion of DNA end resection by BRCA1-BARD1 in homologous recombination
- PMID: 39261729
- PMCID: PMC11539920
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07910-2
Promotion of DNA end resection by BRCA1-BARD1 in homologous recombination
Abstract
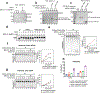
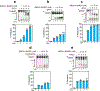
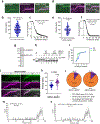
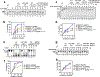
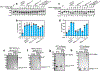
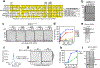
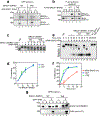
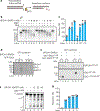
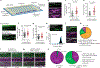
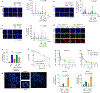
The licensing step of DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination entails resection of DNA ends to generate a single-stranded DNA template for assembly of the repair machinery consisting of the RAD51 recombinase and ancillary factors1. DNA end resection is mechanistically intricate and reliant on the tumour suppressor complex BRCA1-BARD1 (ref. 2). Specifically, three distinct nuclease entities-the 5'-3' exonuclease EXO1 and heterodimeric complexes of the DNA endonuclease DNA2, with either the BLM or WRN helicase-act in synergy to execute the end resection process3. A major question concerns whether BRCA1-BARD1 directly regulates end resection. Here, using highly purified protein factors, we provide evidence that BRCA1-BARD1 physically interacts with EXO1, BLM and WRN. Importantly, with reconstituted biochemical systems and a single-molecule analytical tool, we show that BRCA1-BARD1 upregulates the activity of all three resection pathways. We also demonstrate that BRCA1 and BARD1 harbour stand-alone modules that contribute to the overall functionality of BRCA1-BARD1. Moreover, analysis of a BARD1 mutant impaired in DNA binding shows the importance of this BARD1 attribute in end resection, both in vitro and in cells. Thus, BRCA1-BARD1 enhances the efficiency of all three long-range DNA end resection pathways during homologous recombination in human cells.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AG021890/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA221858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA139429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA246807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA278370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA219836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM115568/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM145432/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM136717/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118026/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES007061/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030432/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA241801/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA236606/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM141091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS119225/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM140264/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R50 CA265315/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244212/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168635/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM128731/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM140127/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA054174/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

