Efficacy and safety of Vonoprazan-based treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 39261752
- PMCID: PMC11389285
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09885-x
Efficacy and safety of Vonoprazan-based treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of the nine most widely studied Vonoprazan (VPZ)-based treatment regimens along with traditional Proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-based treatment regimens in eradicating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
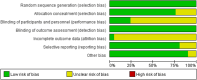
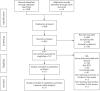
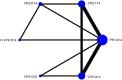
Design: Through searching PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, we exclusively included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to investigate the efficacy of VPZ-based and PPI-based therapies for H. pylori infection. The included studies were evaluated for methodological quality using the Cochrane bias risk assessment tool, and the data analysis software was used to analyze the data accordingly.
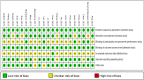
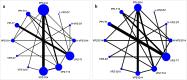
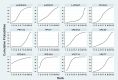
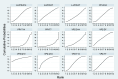
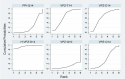
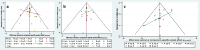
Results: The RCTs were collected from the earliest available date up to August 2023. Twenty-one RCTs were included, with a total sample size of 5481. The results of the network meta-analysis showed that the eradication rate of the VPZ-based quadruple 14-day (VPZ-Q14) treatment regimen in Intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis was the highest (SUCRA: 0.874); The eradication rate of the VPZ-based quadruple 10-day (VPZ-Q10) treatment plan in Per-protocol (PP) analysis was the highest (SUCRA: 0.849). All regimens were well tolerated without significant differences. According to the probability ranking of safety, high-dose VPZ-based dual 14-day therapy (H-VPZ-D14) ranked first in SUCRA, reaching 0.952. This indicates that H-VPZ-D14 treatment is the safest with a relatively low incidence of adverse effect. Therefore, VPZ-based therapies not only have a higher eradication rate, but also possess satisfactory safety.
Conclusion: Compared with traditional PPI-based therapies, VPZ-based therapies have shown superior eradication effects. Based on the Ranking Plot of the Network, the VPZ-Q14 or VPZ-Q10 treatment regimen for H. pylori has a higher eradication rate and acceptable differences compared to other treatment regimens. In addition, for regions with high antibiotic resistance rates, we recommend a 14-day quadruple therapy with bismuth based on VPZ.
Keywords: H. Pylori; Network meta-analysis; PPI-based; VPZ-based.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

