Genetic analysis of QTLs for lysine content in four maize DH populations
- PMID: 39261785
- PMCID: PMC11391625
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10754-9
Genetic analysis of QTLs for lysine content in four maize DH populations
Abstract
Background: Low levels of the essential amino acid lysine in maize endosperm is considered to be a major problem regarding the nutritional quality of food and feed. Increasing the lysine content of maize is important to improve the quality of food and feed nutrition. Although the genetic basis of quality protein maize (QPM) has been studied, the further exploration of the quantitative trait loci (QTL) underlying lysine content variation still needs more attention.
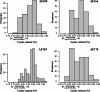
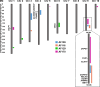
Results: Eight maize inbred lines with increased lysine content were used to construct four double haploid (DH) populations for identification of QTLs related to lysine content. The lysine content in the four DH populations exhibited continuous and normal distribution. A total of 12 QTLs were identified in a range of 4.42-12.66% in term of individual phenotypic variation explained (PVE) which suggested the quantitative control of lysine content in maize. Five main genes involved in maize lysine biosynthesis pathways in the QTL regions were identified in this study.
Conclusions: The information presented will allow the exploration of candidate genes regulating lysine biosynthesis pathways and be useful for marker-assisted selection and gene pyramiding in high-lysine maize breeding programs.
Keywords: Double haploid population; Genetic analysis; Lysine content; Maize; QPM.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Nelson O, Pan D. Starch synthesis in maize endosperms. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 1995;46:475–96. 10.1146/annurev.pp.46.060195.002355 - DOI
-
- Misra PS, Jambunathan R, Mertz ET, Glover DV, Barbosa HM, McWhirter KS. Endosperm protein synthesis in maize mutants with increased lysine content. Sci New Ser. 1972;176:1425–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

