Integrative analysis of the role of the DPH gene family in hepatocellular carcinoma and expression validation
- PMID: 39262488
- PMCID: PMC11385253
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-24-147
Integrative analysis of the role of the DPH gene family in hepatocellular carcinoma and expression validation
Abstract
Background: The diphthamide (DPH) gene family is a group of genes that encode a set of enzymes that specifically modify eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2). Although previous studies have shown a link between the DPH genes (DPHs) and carcinogenesis, it is still unknown how the DPHs affect hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to describe the expression, clinical significance, and potential mechanisms of DPHs in HCC.
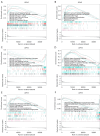
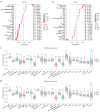
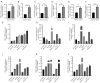
Methods: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx), and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) databases were utilized to research the expression of DPHs in HCC. The relationship between the expression of DPHs and the clinicopathological characteristics of HCC patients was investigated using TCGA data, and their diagnostic value was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and their prognostic value was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier curves and univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Potential reasons for the upregulation of DPH2 and DPH3 (DPH2,3) expression in HCC were analyzed using multiple databases. Additionally, this study also explored the potential biological functions of DPH2,3 in HCC via gene sets enrichment analysis (GSEA). Correlation analysis of DPH2,3 expression with immune-related genes and immune checkpoints was performed using Spearman's correlation analysis, and single-sample GSEA was used to assess the distribution of tumor-infiltrating immune cell types.
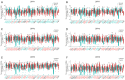
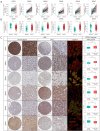
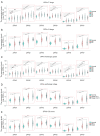
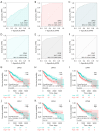
Results: DPH1,7 expression was downregulated in tumor tissues while DPH2,3,5,6 expression was upregulated and showed a similar expression pattern in HCC. The results of the ROC analysis suggested that DPHs had valuable diagnostic properties in HCC. Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that DPH2,3,7 had prognostic predictive value in HCC. Furthermore, univariate and multivariate Cox regression suggested that DPH2,3 was an independent predictive factor for HCC. GSEA analysis revealed that DPH2,3 might be tightly associated with Pathways in cancer, cell cycles, Fc gamma R mediated phagocytosis, etc. Additionally, DPH2,3 expression and numerous immune-related genes showed a positive connection, including chemokines receptor genes, immunosuppressive genes, chemokines genes, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes, and immunostimulatory genes. Further analysis of the association between 24 immune infiltrating cells and DPH2,3 revealed the greatest negative correlation between natural killer (NK) cells and Th17 cells, but the greatest positive correlation with Th2 cells.
Conclusions: DPHs significantly influence the development and progression of HCC. DPH2,3 has significant diagnostic and prognostic potential and may be a promising target for immunotherapy.
Keywords: Diphthamide gene family (DPH gene family); hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); immune cells; immune checkpoints; tumor microenvironment (TME).
2024 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at: https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-24-147/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
