Relationship between visual function and macular microstructure in highly myopic patients undergoing surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment
- PMID: 39262726
- PMCID: PMC11384375
- DOI: 10.62347/SPLN8778
Relationship between visual function and macular microstructure in highly myopic patients undergoing surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the relationship between visual function and macular microstructure in highly myopic patients undergoing surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD).
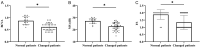
Methods: Fifty-eight highly myopic patients treated in the Baoding No. 1 Central Hospital between December 2021 and September 2023 were selected as the research participants for retrospective analysis. All patients were complicated with RRD and underwent retinal reattachment surgery at Baoding No. 1 Central Hospital after diagnosis. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) examinations were performed before and 3 months after surgery, and visual field mean sensitivity (MS) and fixation stability (FS) were measured by microperimetry. Additionally, changes in postoperative macular microstructure and micro blood flow were determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT), and their correlations with visual function were analyzed.
Results: Patients showed reduced BCVA, MS, and FS after surgery (all P<0.05), with 70.69% of them presenting with macular microstructural changes, mainly ellipsoid zone disruption and external limiting membrane disruption. Patients with macular microstructural changes exhibited significantly decreased BCVA, MS, and FS than those without (all P<0.05). In terms of micro blood flow, the BCVA, FS, and MS of patients with macular microstructural changes were negatively correlated with the foveal avascular zone (FAZ) area but were positively related to FAZ morphological index, PSCP, and VSCP (all P<0.05).
Conclusions: Changes in patients' visual function after surgery for RRD can be effectively evaluated by observing the macular ellipsoid, the integrity of the external limiting membrane, and the alterations in micro-blood flow, enabling the formulation of early and targeted interventions.
Keywords: High myopia; foveal avascular zone; macular microbleed; macular microstructure; rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Lin F, Chen S, Song Y, Li F, Wang W, Zhao Z, Gao X, Wang P, Jin L, Liu Y, Chen M, Liang X, Yang B, Ning G, Cheng CY, Healey PR, Park KH, Zangwill LM, Aung T, Ohno-Matsui K, Jonas JB, Weinreb RN, Zhang X Glaucoma Suspects with High Myopia Study Group. Classification of visual field abnormalities in highly myopic eyes without pathologic change. Ophthalmology. 2022;129:803–812. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ng DSC, Chan LKY, Lai TYY. Myopic macular diseases: a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023;51:229–242. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XJ, Chen XN, Tang FY, Szeto S, Ling XT, Lin ZX, Tham CC, Pang CP, Chen LJ, Yam JC. Pathogenesis of myopic choroidal neovascularization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surv Ophthalmol. 2023;68:1011–1026. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Medrano J, Montero JA, Flores-Moreno I, Arias L, Garcia-Layana A, Ruiz-Moreno JM. Myopic maculopathy: current status and proposal for a new classification and grading system (ATN) Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019;69:80–115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
