The mitochondrial stress signaling tunes immunity from a view of systemic tumor microenvironment and ecosystem
- PMID: 39262792
- PMCID: PMC11388186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110710
The mitochondrial stress signaling tunes immunity from a view of systemic tumor microenvironment and ecosystem
Abstract
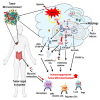
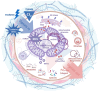
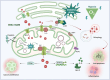
Mitochondria play important roles in cell fate, calcium signaling, mitophagy, and the signaling through reactive oxygen species (ROS). Recently, mitochondria are considered as a signaling organelle in the cell and communicate with other organelles to constitute the mitochondrial information processing system (MIPS) that transduce input-to-output biological information. The success in immunotherapy, a concept of systemic therapy, has been proved to be dependent on paracrine interactions within the tumor microenvironment (TME) and distant organs including microbiota and immune components. We will adopt a broader view from the concept of TME to tumor micro- and macroenvironment (TM 2 E) or tumor-organ ecosystem (TOE). In this review, we will discuss the role of mitochondrial signaling by mitochondrial ROS, calcium flux, metabolites, mtDNA, vesicle transportation, and mitochondria-derived peptide in the TME and TOE, in particular immune regulation and effective cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: Cancer; Immune response; Microenvironment.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Margulis L. Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology; 1975. Symbiotic Theory of the Origin of Eukaryotic Organelles; Criteria for Proof; pp. 21–38. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

