A Comparative Ex Vivo Study on Apex Locator Precision in Mature Teeth and Immature Teeth With Divergent Canals
- PMID: 39262938
- PMCID: PMC11390146
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.69116
A Comparative Ex Vivo Study on Apex Locator Precision in Mature Teeth and Immature Teeth With Divergent Canals
Abstract
Aim: This study investigates the accuracy of an apex locator in mature and immature teeth with divergent root canals ex vivo.
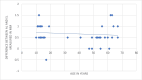
Materials and methods: Fifty extracted premolar teeth were utilized for the study, with 25 mature teeth (Nolla stage 9 or 10) and 25 immature teeth (Nolla stages ≤ 8). The discrepancies between the actual length (AL) and the electronic length (EL), measured using a Bingo 1020 apex locator, were compared and analyzed. Statistical analysis included Pearson's correlation analysis, a T-test for independent samples, and multiple linear regression. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
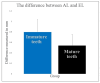
Results: The difference between AL and EL in immature teeth was significantly higher than in mature premolar teeth. Nonetheless, patient gender or jaw type (upper/lower) did not affect the accuracy of electronic apex locator (EAL) measurements.
Conclusion: EAL readings are less accurate in immature teeth than in mature teeth. Supplementary measures, such as radiographic length determination and wet-dry paper point tests, are required to confirm the working length for improved treatment outcomes and patient compliance.
Keywords: accuracy; electronic apex locators; ex vivo; immature teeth; tooth development.
Copyright © 2024, Kaufman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Hadassah Medical Center Ethics Committee issued approval HMO-21-0583. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of a new apex locator: an in vitro study.Int Endod J. 2002 Feb;35(2):186-92. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2591.2002.00468.x. Int Endod J. 2002. PMID: 11843975
-
Comparison of Radiovisiography, an Apex Locator and an Integrated Endomotor-inbuilt Apex Locator in Primary Teeth Endometrics.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022;15(Suppl 1):S18-S21. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2123. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35645506 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of an Electronic Apex Locator (EAL) in Measuring the Working Length of Root Canals in Comparison With Radiographs: An In Vivo Study.Cureus. 2024 May 14;16(5):e60283. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60283. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38872664 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of working length for teeth with wide or immature apices: a review.Int Endod J. 2013 Jun;46(6):483-91. doi: 10.1111/iej.12032. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Int Endod J. 2013. PMID: 23216284 Review.
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locator and Digital Radiography for Working Length Determination in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review.J Dent (Shiraz). 2024 Sep 1;25(3):203-214. doi: 10.30476/dentjods.2023.97323.2006. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Dent (Shiraz). 2024. PMID: 39371951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Factors that affect the outcomes of root canal treatment and retreatment - a reframing of the principles. Gulabivala K, Ng YL. Int Endod J. 2023;56 Suppl 2:82–115. - PubMed
-
- Factors affecting the long-term results of endodontic treatment. Sjögren U, Hägglund B, Sundqvist G, Wing K. J Endod. 1990;16 - PubMed
-
- Electronic apex locators. Gordon MP, Chandler NP. Int Endod J. 2004;37:425–437. - PubMed
-
- Determination of working length for teeth with wide or immature apices: a review. Kim YJ, Chandler NP. Int Endod J. 2013;46:483–491. - PubMed
-
- Critical diameter of apical foramen and of file size using the Root ZX apex locator: an in vitro study. Herrera M, Ábalos C, Lucena C, Jiménez-Planas A, Llamas R. J Endod. 2011;37:1306–1309. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
