Prognostic and predictive significance of soluble programmed death ligand 1 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39263019
- PMCID: PMC11384500
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-24-392
Prognostic and predictive significance of soluble programmed death ligand 1 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have been shown to exhibit elevated levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in the blood, associated with poor survival in NSCLC. The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) composition reflects the tumor microenvironment of lung cancer. In this study, we investigated sPD-L1 levels in BALF and its role as a prognostic and predictive marker in patients with stage IV NSCLC.
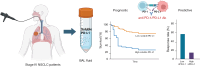
Methods: We prospectively obtained BALF from lung cancer patients who underwent bronchoscopy between January 2020 and September 2022 at Chungnam National University Hospital (CNUH). Finally, 94 NSCLC stage IV patients were included in this study. Soluble PD-L1 levels in BALF were measured using a human PD-L1 Quantikine ELISA kit.
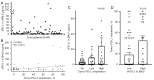
Results: The correlation between PD-L1 expression in tumor cells and sPD-L1 in BALF was weakly positive (rho =0.314, P=0.002). The median overall survival (OS) of the low sPD-L1 in BALF group was 16.47 months [95% confidence interval (CI): 11.15-21.79 months], which is significantly longer than 8.87 months (95% CI: 0.0-19.88 months, P=0.001) in the high sPD-L1 in BALF group. In 64 patients treated with or without immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), sPD-L1 in BALF was significantly associated with progression-free survival (PFS) and OS. In the subgroup analysis of 31 patients treated with ICI, the objective response rate (ORR) in the low sPD-L1 BALF group was significantly higher than in high sPD-L1 in BALF group (ORR: 60.9% vs. 12.5%, P=0.02).
Conclusions: Soluble PD-L1 in BALF is a potential prognostic indicator for patients with stage IV NSCLC and a predictive marker for ICI treatment response.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); biomarker; bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF); soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1).
2024 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-24-392/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
