Safety and efficacy of immunotherapy using a double-dose regimen in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): results of IDEE study
- PMID: 39263023
- PMCID: PMC11384495
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-24-141
Safety and efficacy of immunotherapy using a double-dose regimen in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): results of IDEE study
Abstract
Background: Pembrolizumab 400 mg every six weeks (Q6W) and nivolumab 480 mg every four weeks (Q4W) are used since 2020 and the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. This recommendation relied on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic models. The objective of the IDEE (Immunothérapie Double dose Etendue: Experience bretonne) study is to determine the safety and efficacy of this treatment regimen in real life conditions.
Methods: We conducted an observational, retrospective, multicentric study including 117 patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who received pembrolizumab Q6W or nivolumab Q4W between March 2020 and March 2021.
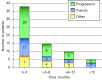
Results: The median age was 67 years, 68% were men with predominantly lung adenocarcinoma. The median time to double-dose regimen failure (TDDF) was 9.2 months. The survival rate at 12 months was 79%. TDDF was not influenced by sex, line of treatment, pathologic subtypes or anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibody. There was no correlation between TDDF and duration of prior exposition to immunotherapy before switching. Sixty-eight patients experienced double-dose treatment failure, 28% because of toxicity including five definitive discontinuations. Five grade ≥3 immune-adverse events were reported included two cases of pneumonitis, all responding to corticosteroid therapy.
Conclusions: Our multicentric cohort supports the feasibility of pembrolizumab Q6W and nivolumab Q4W for patients with advanced NSCLC. There is no warning signal regarding safety neither efficacy in our real-life data.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); extended interval dosing; immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI).
2024 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-24-141/coif). H.L. receives honoraria, participation on Advisory Board and support for meeting travel from Roche, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Astrazeneca, Sanofi. G.D.C. reports participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for MSD, BMS, Roche, Astrazeneca, Takeda and Sanofi and support for attending meetings by Pfizer. C.R. reports consulting fees from Astrazeneca, MSD, Takeda and BMS. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials