Psychosocial determinants of academic achievement in Ethiopian higher education students, 2024. Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39263049
- PMCID: PMC11385848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36465
Psychosocial determinants of academic achievement in Ethiopian higher education students, 2024. Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Ethiopian students' academic achievement goes beyond just cognitive ability. It is interwoven with psychological and social factors. This analysis examines how these interconnected dimensions, including behaviour, emotions, and mental well-being, influence academic attainment. By revealing the multifaceted factors that shape student well-being and success, this review highlights their critical role in the higher education landscape.
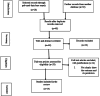
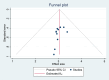
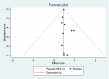
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis study aimed to contribute to the academic literature by exploring the psychosocial factors affecting the academic achievement of Ethiopian higher education students. It leveraged a diverse array of scholarly databases, and adherence to recommended reporting guidelines ensured methodological rigor and transparency throughout the investigation.
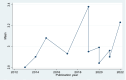
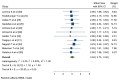
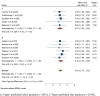
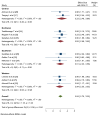
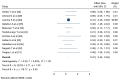
Result: This systematic review synthesizes findings from 14 high-quality Ethiopian cross-sectional studies assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. The overall pooled mean grade point average of respondents was 3.04, [(95 % CI: 2.75, 3.32), I2 = 0.00 %, P < 0.001)]. The pooled odds ratio psychosocial predictors of academic achievement was 0.47, [(95 % CI: 0.46, 0.48), I2 = 0.00 %, P = 0.001)]. The study explored factors affecting academic achievement, including psychological (sleep, stress, self-esteem) and sociological factors (social media, financial hardship, social support). The review found that these factors emerged as significant influences, highlighting the multifaceted nature of academic success.
Conclusion: This synthesized study champions a holistic approach to education, urging the integration of academic progress and student well-being. It emphasizes interventions in mental health, social support, and resource access, and acknowledge their multifaceted impact on learning. In addition, it would be better to build inclusive environments with the involvement of educators and policymakers to optimize the academic success of higher education students.
Keywords: Academic achievement; Ethiopia; Higher education students; Psychosocial predictors.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no apparent conflicts of interest with this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recovery schools for improving behavioral and academic outcomes among students in recovery from substance use disorders: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 4;14(1):1-86. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.9. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131375 Free PMC article.
-
Small class sizes for improving student achievement in primary and secondary schools: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 11;14(1):1-107. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.10. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131395 Free PMC article.
-
The role of demographic and psychosocial factors in academic achievement: insights from a cross-sectional study on physiotherapy and rehabilitation students.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Mar 10;25(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-06958-6. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40065347 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Service learning for improving academic success in students in grade K to 12: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 7;18(1):e1210. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1210. eCollection 2022 Mar. Campbell Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36913211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doran E.E., Hengesteg P.S. Advocating for Mexican American studies in whitestream community colleges: a focus on faculty efforts. Journal of Diversity in Higher Education. 2021;14(1):84.
-
- Burke A. Student retention models in higher education: a literature review. College and University. 2019;94(2):12–21.
-
- Costa C., et al. Estranged students in higher education: navigating social and economic capitals. Camb. J. Educ. 2020;50(1):107–123.
-
- Gómez L.F., Valdés M.G. The evaluation of teacher performance in higher education. Journal of Educational Psychology-Propositos y Representaciones. 2019;7(2):499–515.
-
- Ruiz-Mallén I., Heras M. What sustainability? higher education institutions' pathways to reach the agenda 2030 goals. Sustainability. 2020;12(4):1290.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

