Technical principles, benefits, challenges, and applications of photon counting computed tomography in coronary imaging: a narrative review
- PMID: 39263472
- PMCID: PMC11384460
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-24-52
Technical principles, benefits, challenges, and applications of photon counting computed tomography in coronary imaging: a narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: The introduction of photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) represents the most recent groundbreaking advancement in clinical computed tomography (CT). PCCT has the potential to overcome the limitations of traditional CT and to provide new quantitative imaging information. This narrative review aims to summarize the technical principles, benefits, and challenges of PCCT and to provide a concise yet comprehensive summary of the applications of PCCT in the domain of coronary imaging.
Methods: A review of PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar was performed until October 2023 by using relevant keywords. Articles in English were considered.
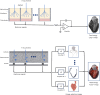
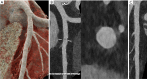
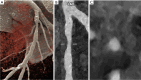
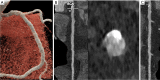
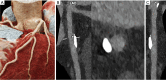
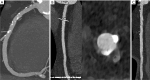
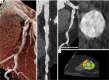
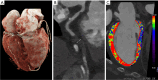
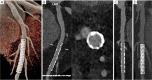
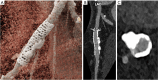
Key content and findings: The main advantages of PCCT over traditional CT are enhanced spatial resolution, improved signal and contrast characteristics, diminished electronic noise and image artifacts, lower radiation exposure, and multi-energy capability with enhanced material discrimination. These key characteristics have made room for improved assessment of plaque volume and severity of stenosis, more precise assessment of coronary artery calcifications, also preserved in the case of a reduced radiation dose, improved assessment of plaque composition, possibility to provide details regarding the biological processes occurring within the plaque, enhanced quality and accuracy of coronary stent imaging, and improved radiomic analyses.
Conclusions: PCCT can significantly impact diagnostic and clinical pathways and improve the management of patients with coronary artery diseases (CADs).
Keywords: Photon-counting detectors; computed tomography angiography (CT angiography); coronary arteries.
2024 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-24-52/coif). F.C. and L.S. serve as unpaid editorial board members of Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy from September 2023 to August 2025. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Brown JC, Gerhardt TE, Kwon E. Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; January 23, 2023.
-
- Budoff MJ, Dowe D, Jollis JG, et al. Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenosis in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter ACCURACY (Assessment by Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography of Individuals Undergoing Invasive Coronary Angiography) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:1724-32. 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.031 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
