Association of serum cystatin C level and major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 39263480
- PMCID: PMC11384458
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-23-482
Association of serum cystatin C level and major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
Background: Recurrent acute myocardial infarction requiring unplanned percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is one of the major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) after PCI. There is a continuing controversy about the association between serum cystatin C, a biomarker for the evaluation of renal function, and the prognosis of ACS patients following PCI. The retrospective study evaluated the association between serum cystatin C level and MACE in ACS patients after PCI.
Methods: Data were retrieved for 330 patients with ACS for primary PCI in a single center. Serum cystatin C levels were measured before PCI. All patients underwent regular follow-ups after PCI, and the studied endpoint was MACE, defined as the need for a repeat revascularization in the heart. The predictive value of serum cystatin C for MACE was analyzed using univariate and multivariate analysis. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis was applied to evaluate the dose-response relationship between serum cystatin C level and MACE in ACS patients following PCI.
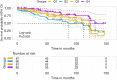
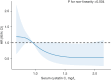
Results: After a median follow-up of 63 months (range, 1-148 months), 121 of the 330 patients experienced MACE. Compared to patients who did not have MACE, patients who had MACE showed a significant decrease in serum cystatin C levels (0.99±0.32 vs. 1.15±0.78 mg/L, P=0.03). In multivariate regression analysis, serum cystatin C level was an independent risk factor for MACE. According to the serum cystatin C level, patients were divided into 4 categories, Cox regression analysis illustrated that the second quartile of serum cystatin C level indicated an increased risk of MACE in patients with PCI for primary ACS compared to the highest quartile [Q2: adjusted hazard ratio (HR) =2.109; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.193-3.727; P=0.01]. RCS analysis showed a significant U-shaped dose-response relationship between cystatin C level and MACE in patients with PCI for ACS (P for non-linearity =0.004).
Conclusions: These results indicated an association between serum cystatin C level and post-PCI MACE in ACS patients.
Keywords: Cystatin C; U-shaped dose-response relationship; acute coronary syndrome (ACS); major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs); percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
2024 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-23-482/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The predictive value of the triglyceride glucose index combined with cystatin C for the prognosis of patients with acute coronary syndrome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 14;15:1423227. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1423227. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39257901 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Calprotectin Levels and Outcome Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Dec 13;25:9517-9523. doi: 10.12659/MSM.918126. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31834876 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet to albumin ratio: A risk factor related to prognosis in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.Int J Cardiol. 2024 Jan 15;395:131588. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.131588. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Int J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37989451
-
Serum cystatin C is associated with the prognosis in acute myocardial infarction patients after coronary revascularization: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Apr 7;22(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02599-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35392813 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of cystatin C in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2021 Mar;51(3):e13440. doi: 10.1111/eci.13440. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33128232
Cited by
-
Correlation of blood lipids, glucose, and inflammatory indices with the occurrence and prognosis of lesion complexity in unstable angina, a retrospective cohort study.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Jan 24;17(1):413-428. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-2122. Epub 2025 Jan 22. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 39975718 Free PMC article.
-
The development and validation of a prognostic prediction modeling study in acute myocardial infarction patients after percutaneous coronary intervention: hemorrhea and major cardiovascular adverse events.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Sep 30;16(9):6216-6228. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-1362. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 39444902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berwanger O, Santucci EV, de Barros E, Silva PGM, et al. Effect of Loading Dose of Atorvastatin Prior to Planned Percutaneous Coronary Intervention on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Acute Coronary Syndrome: The SECURE-PCI Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018;319:1331-40. 10.1001/jama.2018.2444 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
