Machine learning prediction of no reflow in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 39263488
- PMCID: PMC11384450
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-24-83
Machine learning prediction of no reflow in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
Background: No-reflow (NRF) phenomenon is a significant challenge in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI). Accurate prediction of NRF may help improve clinical outcomes of patients. This retrospective study aimed at creating an optimal model based on machine learning (ML) to predict NRF in these patients, with the additional objective of guiding pre- and intra-operative decision-making to reduce NRF incidence.
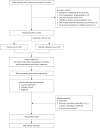
Methods: Data were collected from 321 STEMI patients undergoing pPCI between January 2022 and May 2023, with the dataset being randomly divided into training and internal validation sets in a 7:3 ratio. Selected features included pre- and intra-operative demographic data, laboratory parameters, electrocardiogram, comorbidities, patients' clinical status, coronary angiographic data, and intraoperative interventions. Post comprehensive feature cleaning and engineering, three logistic regression (LR) models [LR-classic, LR-random forest (LR-RF), and LR-eXtreme Gradient Boosting (LR-XGB)], a RF model and an eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model were developed within the training set, followed by performance evaluation on the internal validation sets.
Results: Among the 261 patients who met the inclusion criteria, 212 were allocated to the normal flow group and 49 to the NRF group. The training group consisted of 183 patients, while the internal validation group included 78 patients. The LR-XGB model, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.829 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.779-0.880], was selected as the representative model for logistic regression analyses. The LR model had an AUC slightly lower than XGBoost model (AUC 0.835, 95% CI: 0.781-0.889) but significantly higher than RF model (AUC 0.731, 95% CI: 0.660-0.802). Internal validation underscored the unique advantages of each model, with the LR model demonstrating the highest clinical net benefit at relevant thresholds, as determined by decision curve analysis. The LR model encompassed seven meaningful features, and notably, thrombolysis in myocardial infarction flow after initial balloon dilation (TFAID) was the most impactful predictor in all models. A web-based application based on the LR model, hosting these predictive models, is available at https://l7173o-wang-lyn.shinyapps.io/shiny-1/.
Conclusions: A LR model was successfully developed through ML to forecast NRF phenomena in STEMI patients undergoing pPCI. A web-based application derived from the LR model facilitates clinical implementation.
Keywords: Machine learning (ML); ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI); no-reflow (NRF); primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI).
2024 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-24-83/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
